Introduction
The need of health psychology has existed from the very beginning. Since psychology became an independent field of study in the 20th century, psychologists have contributed significantly to understanding why some people fall ill while others do not, how individuals adjust to health conditions, and the factors influencing health-related behaviors.
A specialized unit within the American Psychological Association (APA) was formed to focus on the role of psychology in health. This unit collaborated with social psychologists, counseling psychologists, and clinical psychologists working in healthcare settings. Together, they established the Division of Health Psychology in 1978 within the APA, marking one of the most significant advancements in psychology over the past 50 years.
Read More- Role of Psychology in Health Psychology
Need of Health Psychology
There are four main reasons why health psychology is essential-
- Changes in Health Patterns
- Advancements in Technology and Research
- Expansion of Healthcare Services
- Increased Medical Acceptance
- Influence of Psychological Factors on Health
- Health Behavior Change and Disease Prevention
- Cultural and Social Determinants of Health
- Role of Health Psychology in Pain Management
- Impact of Digital Health and Telemedicine
- Psychological Support for Terminal Illness and Palliative Care
Let’s explore these factors in detail.
1. Changes in Health Patterns
Until the 20th century, acute diseases like tuberculosis, influenza, and measles were widespread. These acute disorders were short-term illnesses caused by viral or bacterial infections and were relatively simple to treat. With advancements in public health, including improved sanitation and waste management, these diseases are now largely under control.
However, chronic illnesses such as heart disease, respiratory diseases, cancer, stroke, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and self-harm are on the rise. Unlike acute diseases, chronic conditions develop slowly and often persist for many years, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life.

Acute and Chronic Illnesses
Health psychology is crucial because-
- Many chronic illnesses have psychological and social causes. For example, unhealthy habits like smoking, alcohol consumption, drug use, and unprotected sex contribute to heart disease, cancer, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), and AIDS.
2. Advancements in Technology and Research
Health psychologists address challenges arising from scientific advancements, new medical technologies, and evolving treatment options.
- Recent research has identified various genes linked to different types of cancer, enabling early detection and risk assessment.
- For instance, how should we support a college student whose mother has just been diagnosed with breast cancer in understanding her own risk? How will a positive genetic test impact her mental well-being? Health psychologists help address such concerns.
- Additionally, gene-editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 offer hope for treating genetic diseases by modifying specific genes responsible for certain conditions.
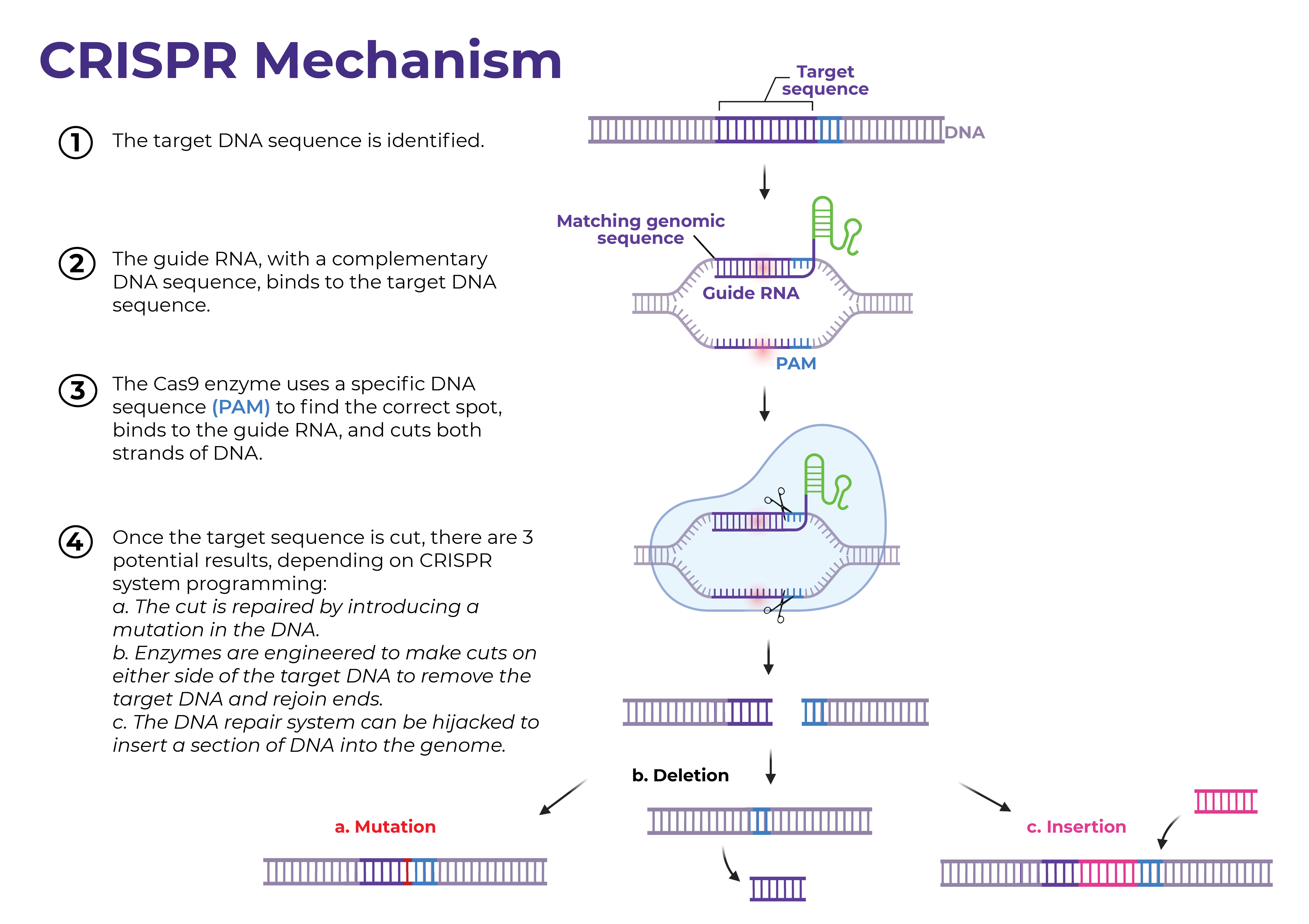
CRISPR Mechanism
However, such advancements also raise ethical and psychological questions that health psychologists help navigate.
While some treatments extend life expectancy, they can also reduce quality of life. Health psychologists assist patients in making informed decisions about life-sustaining measures and provide counseling to help them cope with the psychological effects of medical conditions.
3. Expansion of Healthcare Services
Healthcare is the largest service industry in the United States, with annual spending exceeding $2.3 trillion (National Center for Health Statistics, 2011).
In India, the healthcare sector has been growing at a CAGR of 22% since 2016, directly employing 4.7 million people. The industry had the potential to generate 2.7 million additional jobs between 2017-2022, reaching $372 billion in 2022 (NITI Aayog, 2022).
Despite this expansion, disparities in healthcare access persist. There is an unequal distribution of medical facilities among different economic classes, making healthcare psychology even more critical.
Health psychology plays a vital role in-
- Prevention – Encouraging behavioral changes before illnesses develop, thereby reducing healthcare costs.
- Improving Patient Satisfaction – Understanding what makes people happy or dissatisfied with their medical care and creating a more user-friendly healthcare system.
Since nearly everyone interacts with the healthcare system at some point, health psychology has a significant influence on overall public well-being.
4. Increased Medical Acceptance of Health Psychology
Another major factor contributing to the rise of health psychology is its growing acceptance within the medical community.
Health psychologists have developed various short-term and long-term behavioral therapies, such as:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
These therapies help manage pain, change unhealthy habits (e.g., smoking), and alleviate treatment side effects. Simple psychological interventions can have long-term positive effects on health.
For example, therapies targeting risk factors like poor diet and smoking have significantly reduced the incidence of illnesses such as coronary heart disease.
To thrive as a field, health psychology must demonstrate its effectiveness both in research and in real-world interventions (Glasgow, 2008; King, Ahn, Atienza, & Kraemer, 2008). It continues to fulfill both roles successfully.
5. Influence of Psychological Factors on Physical Health
Psychological factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and personality traits, significantly impact physical health (Taylor, 2018). Chronic stress, for example, has been linked to high blood pressure, heart disease, and weakened immune function (Cohen, Janicki-Deverts, & Miller, 2007).
- Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) research shows that psychological stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and slower recovery from illnesses (Segerstrom & Miller, 2004).
- Emotional regulation and coping mechanisms play a crucial role in managing diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune disorders (Kiecolt-Glaser, McGuire, Robles, & Glaser, 2002).
Thus, health psychology helps develop strategies to manage stress and improve overall well-being.
6. Health Behavior Change and Disease Prevention
Unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise, and substance abuse contribute to numerous chronic illnesses (Ogden, 2017). Health psychology focuses on understanding and changing these behaviors using evidence-based interventions.
- The Health Belief Model (HBM) and Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) help explain why people engage in certain health behaviors and how to encourage positive changes (Glanz, Rimer, & Viswanath, 2015).
- Behavioral interventions like motivational interviewing, habit formation techniques, and digital health apps have proven effective in promoting healthier lifestyles (Schüz, Brick, Wilding, & Conner, 2021).
By targeting modifiable risk factors, health psychology contributes to reducing disease prevalence and healthcare costs.
7. Cultural and Social Determinants of Health
Health is shaped by cultural norms, socioeconomic status, and environmental factors (Marmot, 2005). Health psychology examines how these social determinants influence health outcomes and access to care.
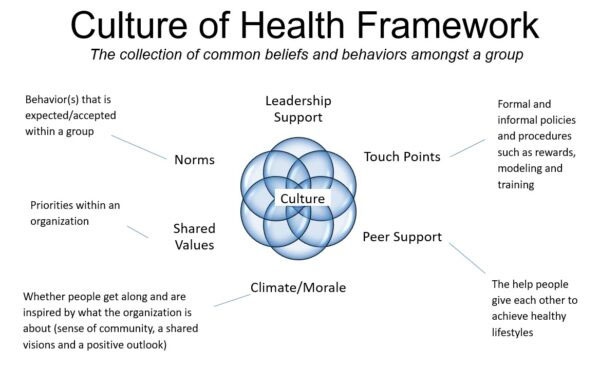
Culture and Health
- Low-income individuals often experience higher levels of stress and limited healthcare access, leading to worse health outcomes (Adler & Rehkopf, 2008).
- Cultural beliefs affect how people perceive illness, treatment, and mental health, influencing health-seeking behaviors (Kleinman, 1980).
Health psychologists work to reduce health disparities by developing interventions that consider these cultural and social influences.
8. Role of Health Psychology in Pain Management
Pain is not just a physical experience—it has psychological, emotional, and social dimensions (Gatchel, Peng, Peters, Fuchs, & Turk, 2007). Health psychology plays a crucial role in:
- Chronic pain management through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness, and relaxation techniques (Eccleston, Morley, & Williams, 2013).
- Reducing opioid dependence by offering non-pharmacological pain relief methods (Turk & Wilson, 2010).
- Helping patients cope with post-surgical pain through psychological interventions (Keefe, Main, & Gil, 2018).
By integrating psychological approaches with medical treatment, health psychology improves pain management and patient recovery.
9. Impact of Digital Health and Telemedicine
With the rise of digital health technologies, health psychology is increasingly involved in designing and evaluating mobile health (mHealth) apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine services (Doherty, 2020).
- Digital interventions help individuals monitor stress, sleep, physical activity, and chronic diseases (Firth et al., 2019).
- Telehealth platforms use psychological principles to enhance patient engagement and treatment adherence (Webb, Joseph, Yardley, & Michie, 2010).
Health psychology ensures that digital health tools are user-friendly, effective, and behaviorally engaging, making healthcare more accessible and personalized.
10. Psychological Support for Terminal Illness and Palliative Care
Health psychology plays a crucial role in helping patients and their families cope with terminal illnesses such as cancer, advanced neurological disorders, and end-stage organ diseases. Psychological support improves emotional well-being, decision-making, and quality of life for both patients and caregivers (Breitbart et al., 2018).
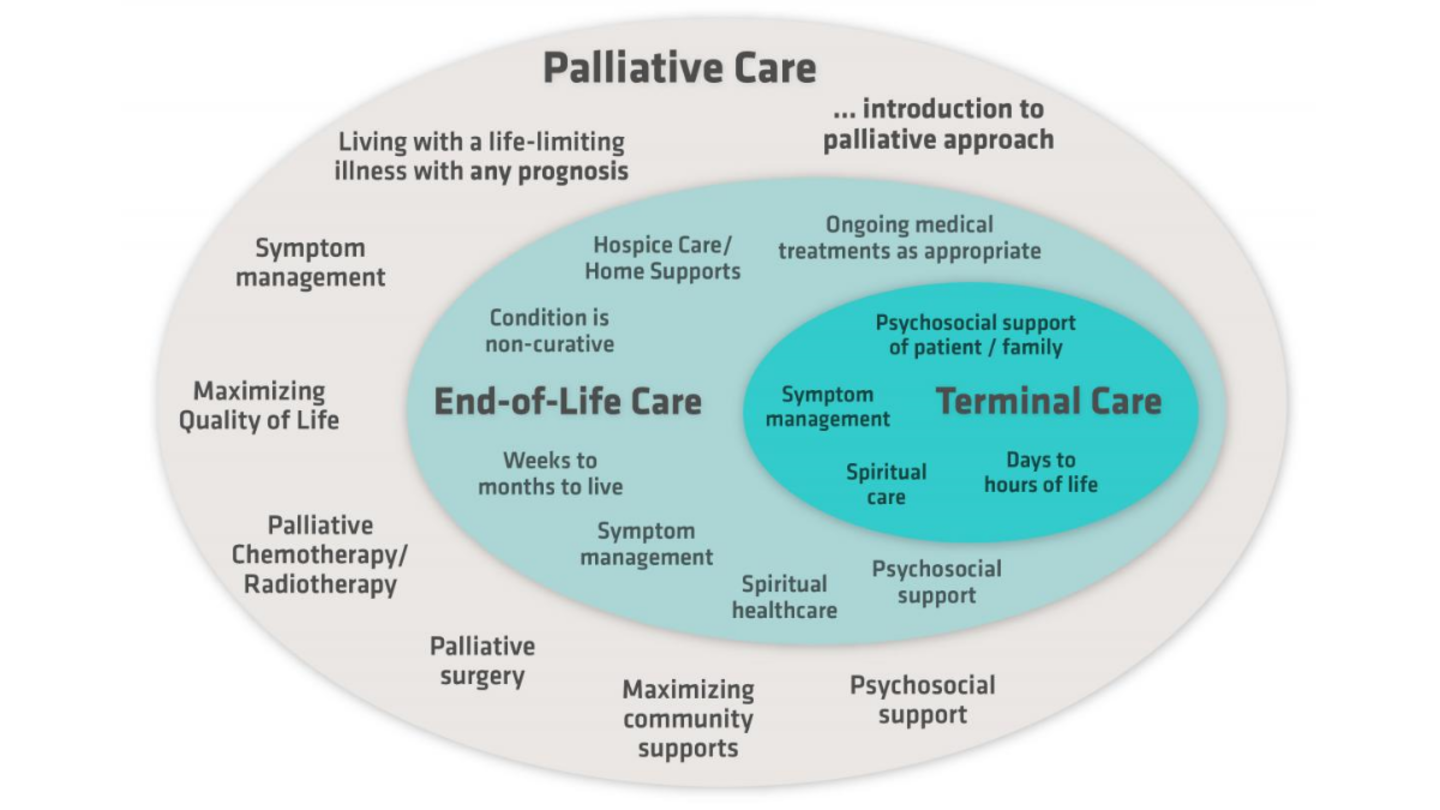
End of the Life Care
- Managing End-of-Life Anxiety – Many terminally ill patients experience depression, anxiety, and fear of death. Health psychologists provide therapies like Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and Meaning-Centered Therapy (MCT) to help patients find peace and purpose in their remaining time (Kissane et al., 2010).
- Grief and Bereavement Support – Families of terminally ill patients often struggle with anticipatory grief. Counseling helps them process emotions and prepare for loss (Holland, 2018).
- Improving Palliative Care Decisions – Patients and families often face difficult decisions regarding hospice care, life-sustaining treatments, and advance directives. Health psychologists assist in these discussions, ensuring that patients’ emotional and psychological needs are addressed (Hudson et al., 2018).
By addressing the psychological aspects of terminal illnesses, health psychology contributes to a more compassionate and holistic approach to healthcare.
Conclusion
Health psychology plays a vital role in understanding the complex relationship between psychological, social, and biological factors in health and illness. From addressing chronic diseases and promoting healthy behaviors to integrating mental health support in medical care, health psychologists contribute significantly to disease prevention, treatment adherence, pain management, and overall well-being. With advancements in technology, expanding healthcare services, and increasing acceptance of psychological interventions, the field continues to grow and evolve.
References
Ogden, J. (2017). Health psychology: A textbook (4th ed.). McGraw Hill Education.
Sarafino, E. P., & Smith, T. W. (2012). Health Psychology – Biopsychosocial Interaction (7th ed.). Wiley India Edition.
Taylor, S. E. (2018). Health Psychology (10th ed.). McGraw Hill Higher Education. Indian Edition.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,430 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2022, November 26). Need of Health Psychology- 10 Important Reasons. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/what-is-the-need-of-health-psychology/
