Introduction to Psychology and Health
Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes, encompassing a vast range of topics including perception, cognition, emotions, social interactions, and individual behaviors. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), health is defined as a “complete state of physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” This comprehensive understanding of health highlights the importance of psychology in addressing not just physical health but also psychological and social factors, which play a crucial role in overall well-being. As our understanding of the interconnections between mind and body evolves, the role of psychology in health care becomes increasingly significant.
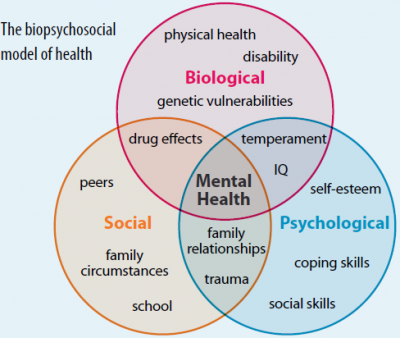
Biopsychosocial Model
While the biomedical model of health care has historically focused on the physical aspects of disease and treatment, this model alone is insufficient in addressing the full range of factors that influence a person’s health. The biopsychosocial model, introduced as an expansion of the biomedical model, offers a more holistic approach to health by considering biological, psychological, and social factors in both the understanding and treatment of illness. This integrated approach emphasizes that health should be viewed not just in terms of physical symptoms but also the psychological and social contexts in which individuals live.
Read More- Health Psychology
Role of Psychology in Health Care
Psychologists play a critical role in promoting health, preventing disease, and improving patients’ quality of life. Their contributions extend far beyond traditional mental health care to encompass the broader landscape of physical health care, where they assist with a variety of psychological issues that affect physical health. These issues can range from behavioral concerns to emotional distress, and psychologists are instrumental in addressing these challenges, often working within interdisciplinary health care teams.
Key roles that psychologists play in health care include-

Psychology in Health Care
- Promotion of Healthy Behavior- Psychologists are essential in designing and implementing interventions that encourage healthier lifestyles. This can involve strategies for improving diet, increasing physical activity, and addressing behaviors that contribute to conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Disease Prevention- Psychology contributes significantly to preventing disease by identifying and addressing the psychological factors that can lead to unhealthy behaviors. For example, psychologists can help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and depression, which can contribute to risk behaviors like smoking, overeating, or substance abuse.
- Improving Quality of Life- Psychologists also help improve patients’ quality of life by assisting them in coping with the emotional, social, and psychological challenges of living with chronic conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, or diabetes. Through psychological interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychologists can help patients manage symptoms, cope with the emotional burden of illness, and enhance their ability to engage in meaningful activities.
Psychologists’ work in health care is guided by ethical principles and a strict code of conduct, ensuring that their interventions are both effective and respectful of patients’ rights and needs. Psychologists are also highly trained to assess, diagnose, and treat a wide range of behavioral and emotional issues that can arise in the context of both physical and mental health concerns.
Psychology in Interprofessional Health Care
As the healthcare system evolves, there is a growing recognition of the importance of an integrated approach to health care. Psychologists, as part of interprofessional care teams, contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of health by addressing the psychological, social, and emotional dimensions of health and illness.
- Integrated Health Care- Psychologists play a pivotal role in integrated health care settings, where the focus is on treating the whole person. By considering not only the physical but also the psychological and social aspects of health, psychologists help to address the complete health state of an individual. This integrated approach leads to better health outcomes and provides patients with more holistic care.
- Primary Care- Psychologists contribute significantly to primary care settings by offering mental and behavioral health services. By identifying and modifying unhealthy behaviors, psychologists help individuals across the lifespan to promote health and wellness. They can also address mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress, which can impact overall physical health.

Integrated Healthcare System
Role of Psychology in Specific Health Conditions
Psychologists play a significant role in managing a variety of health conditions, helping to improve patients’ psychological well-being and ultimately their physical health.
1. Alzheimer’s Disease- Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia present complex challenges for both patients and their families. Psychologists with specialized training in cognitive testing and neuropsychological evaluation are instrumental in differentiating between normal age-related cognitive changes, dementia, and other mental health conditions. Early identification and intervention can help improve the quality of life for both patients and their caregivers.
2. Cancer-
- Pediatric Cancer- Psychologists help identify adjustment difficulties in children with cancer and provide psychological interventions for depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress. They also assist with problem-solving for the child and their family, offering emotional support during treatment and survivorship.
- Adult Cancer- Psychologists play a leading role in developing evidence-based treatments for cancer patients, including those addressing neurocognitive impairments that may arise as a result of cancer or its treatment. They also provide interventions to help cancer patients cope with the emotional challenges of diagnosis and treatment.
- Breast Cancer- Psychologists use diagnostic measures and interviewing techniques to assess psychosocial distress and body image concerns in breast cancer patients, helping them to manage the emotional and psychological challenges associated with their condition.
- Colorectal Cancer- Psychological interventions, such as CBT and relaxation training, are shown to reduce psychological distress, improve self-esteem, and enhance the social functioning and self-efficacy of colorectal cancer patients.
3. Cardiac Health- There is a well-established link between depression and heart disease, with depression often exacerbating the risk factors for cardiovascular conditions. Psychotherapy has been shown to be effective in reducing these risk factors, improving both mental and physical health outcomes.
4. Liver Transplantation- In the context of liver transplantation, psychologists play a key role in pre-transplant assessments, helping to ensure that patients are mentally and emotionally prepared for the procedure. Post-transplant care also involves addressing psychological concerns that may arise during recovery, thereby improving long-term outcomes.
5. Obesity-
- Childhood and Adolescent Obesity- Psychologists work with children, adolescents, and their families to address the psychological and social factors that contribute to obesity. They help with motivation, behavior change, and emotional functioning to support healthier lifestyles.
- Adult Obesity- In adults, psychologists provide critical support in weight-loss programs, helping individuals to adhere to dietary plans, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and manage the psychological aspects of weight control, which are crucial in addressing the obesity epidemic.

Interactive Perspective to Obesity
6. Pain Management- Chronic pain is a complex issue that involves both physical and psychological components. Psychologists use evidence-based therapies, such as CBT and self-regulatory strategies, to help patients manage pain, reduce distress, and improve quality of life.
7. Perinatal Depression- Depression during pregnancy and the postpartum period is common but often overlooked. Psychologists play a critical role in providing psychotherapeutic interventions for perinatal depression, as recent guidelines recommend non-pharmacological treatments to minimize risks to both the mother and child.
8. Pressure Ulcers- Pressure ulcers, or bedsores, can be prevented and treated through behavioral interventions. Psychologists work with healthcare teams to implement strategies that reduce the risk of pressure ulcers, thereby decreasing hospital stays and healthcare costs.
9. Presurgical Conditions- In some cases, psychological evaluations are essential before surgical procedures, particularly for spinal conditions. Psychological assessments help predict surgical outcomes and ensure that patients are psychologically prepared for the surgery.
10. Pediatric Sleep Disorders- Psychologists can evaluate and treat pediatric sleep disorders, helping children and their families address both the behavioral and cognitive factors that contribute to sleep difficulties. Effective treatment can improve sleep quality and overall health.
Conclusion
Until the mid-1960s, the role of psychologists in healthcare was primarily focused on assessing and treating mental health issues. However, as knowledge about the interaction between psychological and physical health has expanded, psychologists have increasingly become an integral part of the healthcare team. The biopsychosocial model has driven this shift, highlighting the importance of addressing not just physical symptoms but also psychological and social factors in the treatment of illness.
Today, psychologists are recognized as key contributors to improving patient outcomes across a wide range of medical conditions. Their expertise in behavior, emotion, and cognition is crucial in promoting health, preventing disease, and improving the quality of life for individuals facing physical health challenges. As the healthcare system continues to evolve, the role of psychology will only become more important, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of their well-being.
References
Ogden, J. (2017). Health psychology: A textbook (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Sarafino, E. P., & Smith, T. W. (2012). Health Psychology: Biopsychosocial Interaction (7th ed.). Wiley India Edition.
Taylor, S. E. (2018). Health Psychology (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Wahass, S. H. (2005). The role of psychologists in health care delivery. Journal of Family & Community Medicine, 12(2), 63-70.
American Psychological Association (APA). (n.d.). The role of psychology in health care. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/health/briefs
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,504 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2022, November 19). 3 Important Role of Psychology in Health. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/role-of-psychology-in-health/
