Purpose of the Test
To Screen the respondents on cognitive skills in the domains of Attention, Language, Memory, Spatial and Executive functions by using Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) by Robert Stern & Travis White (2003)
Introduction
- Neuropsychological Assessment
- Neuroanatomy
- Types of Nervous system : CNS, PNS and ANS
- Brain Lobes & Functions
- Neuroimaging techniques : CT, MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG
- Neuropsychological Disorders
- Dementia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
- Traumatic Brain injury
- Neuropsychological Testing
- Approaches
- Applications
- Classical Neuropsychological Tests
- Bender-Gestalt Test
- Luria Neuropsychological Battery
- Halstead- Reitan Neuropsychological Battery
Test Description of NAB
- Authors : Robert Stern & Travis White
- Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) is a comprehensive battery for assessment of cognitive skills and functions in adults, aged 18 to 97 yrs. with known or suspected disorders of CNS.
- Structure of NAB : NAB consists of 6 Modules
- Screening Module
- 5 Domain Specific Modules
- Attention Module
- Language Module
- Memory Module
- Spatial Module
- Executive functions Module
Screening Module has 5 Domains :
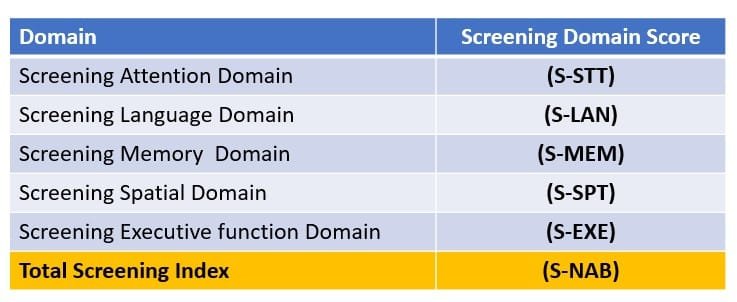
Screening Domain Score summary
Results of screening module are used to determine whether additional, in-depth, follow up examination is necessary. The main NAB modules are administered for the specific range of screening domain scores :
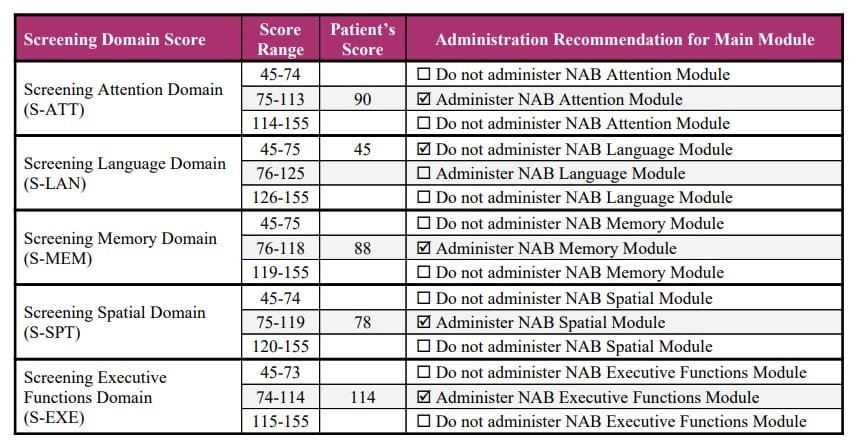
High screening domain scores rejects the possibility of any neurodevelopment disorder or cognitive dysfunctions, while very low score confirms the cognitive dysfunction and such individual might not be helped with further administration of main domains.
Psychometric Properties
Reliability
The reliability of the test shows the consistency, accuracy, homogeneity and temporal stability of test scores across situations (Anastasi & Urbina, 1997).
Internal consistency Reliability : The homogeneity for each subtest was determined using Cronbach alpha coefficients (Cronbach, 1951). The Form 1 and Form 2 average screening Modules alpha range from 0.24 (Screening Discrimination) to 0.79 (Screening Digit Backward).
Though many NAB primary subtests are excluded from internal consistency for variety of reasons like use of unique item presentation formats, inter-item dependency (*which will artificially inflate reliability) and use of speed of performance formats.
Test Retest Reliability : The test retest reliability is derived for Form 1 as well as Form 2 and sampling across a wide age range, exceeding the period of 6 months. The corrected test retest reliability for Average age group ranges from 0.71 (screening numbers and letters efficiency) to 0.11 (screening shape learning immediate recognition).
Changes in the test scores after retesting reflect changes in the individual’s cognitive ability, the practise effect and/or other situational variables.
Equivalent Form Reliability : NAB has to equivalent forms – Form 1 and Form 2, whose reliability was test using generalizability coefficient. The median G coefficient for the screening module primary score is 0.75, which demonstrates very good reliability.
Validity
NAB has provided evidences for several different validities such as content validity, construct validity and criterion validity.
Demographically Corrected Norms
Demographically corrected Norms are established on sample of 1448 individuals. Results are needed to interpret within context of an age, educational attainment and sex. Manual of NAB (Demographically Corrected Norms) contains separate normative tables for all the combinations of Age, Education and sex.
Methodology
Material for Screening Module
- 4 NAB manuals
- Administration, Scoring and interpretation manual
- Technical manual (Reliability & Validity)
- Demographically corrected Norms manual
- US census manual
- Record form (For examiner)
- Response Sheer (For examinee)
- Stimulus Book
- Test Manipulatives (#Tans, #Maps)
- Scoring Templates
- Score Summary & Profile Form
- Stopwatch
- Wooden Screen
- Stationary
Case History
- What is your age, gender, and educational background?
- Have you ever been diagnosed with any medical, neurological, or psychiatric condition?
- Do you have difficulty staying focused on tasks or conversations?
- How often do you find yourself becoming easily distracted by your surroundings?
- Do you have trouble understanding conversations or instructions?
- Do others often ask you to repeat yourself because they don’t understand what you’re saying?
- Do you frequently forget recent events or conversations?
- How often do you misplace items such as keys or your phone?
- Have you experienced difficulty recalling names, dates, or appointments?
- Do you have trouble judging distances or navigating familiar environments?
- Do you have trouble recognizing familiar faces or locations?
- Have you noticed problems with tasks that involve visual or spatial coordination, such as driving or using tools?
- Do you have difficulty organizing your daily tasks or keeping track of responsibilities?
- How do you handle situations that require problem-solving or quick decision-making?
- Have you noticed difficulty adapting to changes in plans or routines?
Procedure
All the required material was checked and arranged properly beforehand. The subject was called inside the cubicle and rapport was established. Prior to administration, the relevant case history was taken. The demographic and background information given at the cover page of Screening module record form was carefully noted.
Test administration :
Order of Administration of 14 sub-tests : As per the Record Form
- Screening Orientation – Self, Time, Situation (Attention)
- Screening Digits Forward (Attention)
- Screening Digits Backward (Attention)
- Screening Auditory Comprehension – Colours, Shapes (Language)
- Screening Shape Learning Immediate Recognition (Memory)
- Screening Story Learning Immediate Recall (Memory)
- Screening Maze (Executive Function)
- Screening Numbers & Letters (Part A) and (Part B) (Attention)
- Screening Shape Learning delayed Recognition (Memory)
- Screening Story Learning delayed Recall (Memory)
- Screening Naming (Language)
- Screening Name/ word generation (Executive Function)
- Screening Design Construction (Spatial function)
- Screening Visual Discrimination (Spatial function)
Scoring For NAB screening module
- The respective raw scores were converted into z scores according to age, education level and sex of the subject using demographically corrected norms.
- These z scores are further converted into the T-scores and percentiles.
- All the required T-scores are added for each domain separately and later converted into Standard scores (S-ATT, S-LAN, S-MEM, S-SPT and S-EXE) and percentile ranks.
- The standard scores of all the added together to derive Total Screening Index i.e S-NAB.
S-NAB = S-ATT + S-LAN + S-MEM + S-SPT + S-EXE
The T-scores & standard scores for each domain are filled in the profile form and further recommendation for administration of specific module were provided.
Precautions
- Environment should be distraction free.
- Rapport should be established before the testing.
- Relevant case history should be taken.
- Standardized instructions should be given.
- Record the responses of the subject carefully, along with qualitative features if present.
- Follow the Discontinuation rule precisely.
- The arrangement of materials like stimulus book, tans, etc. must according to handedness of the subject.
- The demographically Corrected norms should be used for interpretation of results.
Instructions
As per the Administration, scoring and interpretation Manual. Read instructions carefully, given in the Bold letters.
For Example, Administration instruction for Screening Orientation:
Say, “I am going to ask you few questions. I want you to answer each question as fully as possible.”
Do not correct or reorient examinee until all items have been administered.
Before reading Item 8, say, “Please answer the next few questions without looking at a clock or a watch.”
A numerical response is not acceptable for Item 3 (3-27-78 for March 27, 1978) and Item 10 (today’s date), If this occur, say, “Please say it in words.”
The instructions in the BOLD should read to subject and NOT the remaining part of it, since those are directions for the administrator.
Result Tables

Result Table NAB
Interpretation
The purpose of the test was to screen the respondents on cognitive skills in the domains of Attention, Language, Memory, Spatial and Executive functions by using Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB). The subject was administered with Screening module to detect the cognitive impairment in the key 5 cognitive functions. Any cognitive function suspected to be impaired was recommended for further specific inspection.
The first domain in the Screening module was attention, which had the standard score of ___. Subjects corresponding percentile rank was ___. This shows that subject has impaired/ non-impaired attention function. This was supported by case history where subject claimed to ____________.
The Memory domain had standard score of ______……
The results showed that, attention/ memory/ language/ spatial/ executive function** is the strongest cognitive function individual possesses. Where, ATT/MEM/ LAN/ SPT/ EXE is the weakest of all.
Mention separately if significant impairment is seen. Recommend further administration of specific NAB module.
Conclusion
Hence, all the cognitive functions measured by NAB i.e attention, memory, language, spatial and executive function are non-impaired and subject does NOT require any further administration… (Normal cognitive functioning)
OR
Subject is suspected to have impaired “attention” function and hence further specific NAB attention module should be administrated… (Standard score S-ATT = 75-113)
OR
Subject has severe attention impairment and there is no need to administer NAB attention module to him/her… (S-ATT = 114-155)
References
- Anastasi, A. (1976). Psychological testing. N.D.: Pearson Education.
- Stern, R. A., & White, J. C. (2003). Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) Administration, Scoring, and Interpretation Manual.
- Stern, R. A., & White, J. C. (2003). Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) Technical manual (Reliability & Validity)
- Stern, R. A., & White, J. C. (2003). Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) Demographically corrected Norms manual
- NAB screening Module Report 1
- NAB screening Module Report 2
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 13,999 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, February 1). Sample report : Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) Screening Module. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/neuropsychological-assessment-battery-nab/
