Introduction
Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian children (MISIC) is most accepted IQ test for Indian children based on Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS).
WHAT IS INTELLIGENCE?
Intelligence is an inferred process that humans use to explain the different degrees of adaptive success in people’s behaviour.
It has been defined by various psychologists. They are as follows:
- The ability to judge well, to understand well, to reason well. -by Binet & Simon
- The capacity to form concepts and to grasp their significance.- by Terman (1916)
- The ability of the individual to adapt adequately to relatively new situations in life. -by Pinter (1921)
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for children (WISC)
According to Wechsler “Intelligence is the aggregate or global capacity of the individual to act purposefully, to think rationally and to deal effectively with the environment.” He developed Wechsler Bellevue Intelligence Scale in 1939.He was interested in measuring the intelligence of adults so he designed another scale known as Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS).
The first revised edition was published in 1981- WAIS-R. Another edition was published in 1997- WAIS III. The WISC was originally developed as a downward extension of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale in 1949. WISC was broadly categorized into two parts. They are as follows:
- Verbal Tests – Information, Comprehension, Arithmetic, Similarity, Vocabulary & Digit Span.
- Performance Tests– Picture Completion, Picture Arrangement, Block Design, Object Assembly, Coding, Mazes
POINT SCALE
This test works on the concept of point scale. All items of a particular type are grouped together and are presented in the increasing order of difficulty. A raw score of each test is totalled and then converted into a derived score, called “Scaled Scores” in WISC. This scaled score is converted into IQ’s for verbal, performance and full-scale IQ.
A revised edition was published in 1974, known as WISC-R. It featured the same subtests however the age range was changed from 5-15 to 6-16. Another revised edition was published in 1991 known as WISC III. Currently, we are using WISC IV which was published in 2003.
MALINS INTELLIGENCE SCALE FOR INDIAN CHILDREN (MISIC)
Malin’s has been adapted from the American test WISC developed by Dr. David Wechsler.
The Indian Scale has been constructed by Dr Arthur J. Malin of Nagpur. During adaptation, an almost total revision had to be made of the test, especially of the culturally biased verbal items. So the test was named as Intelligence Scale for Indian Children- ISIC or MISIC. English is the only language that applies universally through India; hence WISC has adapted in English for English Speaking children in India. Later it was also adapted in Hindi and Marathi as India is a country dominated by many regional languages.
MISC is an intelligence test for children from the ages of 6 to 15 years 11 months. It is administered individually and takes about 2 to 2-1/2 hours.
The test comprises of 11 subtests divided into two groups: Verbal Tests & Performance Tests.
I. 6 Verbal Scale consists of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian children
- Information Test
- General Comprehension Test
- Arithmetic Test
- Analogy & Similarity Test
- Vocabulary Test
- Digit Span Test
II. 5 Performance Scale consists of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian children
- Picture Completion Test
- Block Design Test
- Object Assembly
- Coding
- Maze
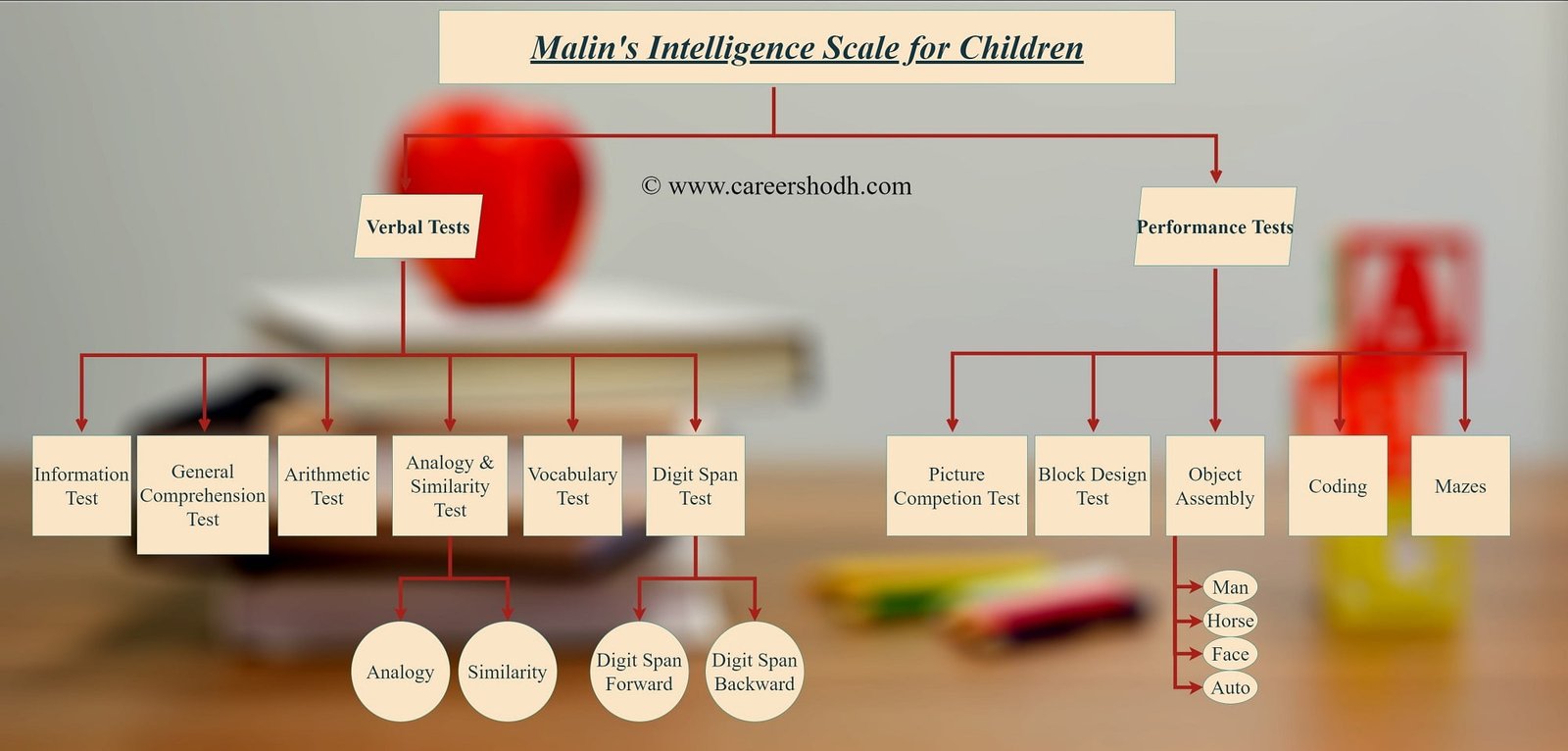
i. Verbal Scales of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children
1. Information Test:
The test consists of questions about factual knowledge of persons, places, and common phenomena. It has total of 30 questions. The test is discontinued after 5 consecutive failures. Questions 1-5 are used for children below 8 years old or suspected mental defects. Each item is scored 1 or 0. The subject above 8 years is given credits for question 1-5 directly, if the subject passes items 6,7 & 8.
Examples- How many ears do you have?
2. General Comprehension Test:
The test consists of questions about certain practices and behavior under certain situations. It measures conventional knowledge and knowledge of social appropriateness. It has total 14 questions. The test is discontinued after 3 consecutive failures. Each item is scored from 0-2. Items 1-5 are scored 2 points if the subject takes personal responsibility; and 1 point if the subjects knows what is to be done, but the responsibility is shirked away. For item 6-14, 2 points are given when the subject gives 2 good reasons , and 1 point when the subject gives one reason.
Example- What should you do if you cut your finger?
3. Arithmetic Test:
The test consists of questions based on simple mathematical calculations which are solved mentally. Problems 1-3 are for the subjects below 8 years or suspected mental defectives. The test is discontinued after 3 consecutive failures. Each item is scored 1 or 0. Credit is given to the subject for the first 3 items if the subject above 8 years solves the item 4 and 5 correctly.
Example- if I break this pencil in half, how many pieces there will be?
4. Analogy & Similarity test:
This test has two subtests, namely Analogy and Similarity, as follows: Analogy: The test consists of 4 incomplete sentences based on analogies that the subject has to complete. The test is for subjects below 8 years old. Each correct analogy is given a score of 2.
Example- Lemon is sour, but sugar is ……….
Similarity: The test consists of questions where the subject has to find the similarity between the two things. It measures verbal concept formation. This test is for subjects above 8 years. Each item is scored from 0-2, depending on the answer. The test is discontinued after 3 consecutive failures or returned to the analogy. If the subject answers the 3 items correctly in similarity, the subject is given the credit for 4 analogies.
5. Vocabulary Test:
The test consists of the question that measures the subject’s general intelligence. It reflects the subject’s breadth of experience and ideas developed over the years. The test has 40 items. Discontinue the test after 5 consecutive failures. Each item is scored from 0 to 2. Except item 1-6 which are scored as 0 or 2. Subject can start directly from 10th item. The subject is credited 2 points directly for the previous 9 items if he/she gives 2 point definition for 10th – 14th items.
Example- Cycle, Shoe, etc.
6. Digit Span Test:
In this test the subject is told a sequence of number verbally. The subject is supposed to repeat the number in the same order. The test is divided into 2 types. They are:
- Digit Span Forward- the digits are repeated as they are called out.
- Digit Span Backward- the digits are repeated in the reverse order.
The score of the test is the highest number of digits repeated without error, both forward and backward digits together.
ii. Performance Scale of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian children
1. Picture Completion Test:
The test consists of twenty pictures in which some part of each picture is missing. The subject is supposed to tell which part of the picture is missing. The subject gets fifteen seconds to examine each picture. The test is discontinued after four failures. Scoring – 1 point is given for each correct response except for last five pictures where an extra bonus score is credited if at least 3 pictures of the last 5 are correct.
2. Block Design Test:
The test consists of 7 coloured blocks and a booklet with pictures of the block arranged according to specific geometric designs. The subject has to arrange the blocks according to the design shown in the picture. The task requires concept formation. Scoring- the subject is given 4 points plus bonus according to the table for design 1 to 7. No points are given for the incomplete design.
3. Object Assembly:
This test consists of puzzles that the subject has to rearrange in meaningful design. It requires visual-motor co-ordination, plan fullness and concept formation. The test has four puzzles. They are mannequin, horse, face and auto.
Scoring differs for each item, as follows:
- Man: For perfect performance, 4 points are rewarded or bonus. 3 points if legs are interchanged or inverted. 2 points if legs or arms are omitted.1 point if the only trunk is correct.
- Horse: Perfect performance is rewarded 6 points or bonus 5 points if the only stomach is inverted 4 points if the midpiece is omitted or legs interchanged. 3 points if the midpiece is inverted and legs interchanged. 2 points if midpiece or leg is omitted.1 point is given for every two pieces joined correctly.
- Face: Perfect performance is awarded 6 points or bonus. 5 points if eyes are inverted or hairpieces omitted. 4 points if mouth and chin omitted. 3 points if large half (2 pieces) are omitted. 1 point if large half and hair are omitted. ½ point is given for each proper joint separate or joined to the whole.
- Auto: Perfect performance is given 6 points or a bonus. 5 points if the door is inverted or reversed. 4 points for omitting pieces 4 & 5 or omitting piece 7. 3 points for omitting 7 and inverting or reversing piece 4, also omitting pieces 4, 5, & 7. 1 point is given for each proper joint.
4. Coding:
The test consists of certain symbols that are paired with numbers or shapes. The subject has to learn them and pair with the appropriate corresponding numbers. Concentration and speed of work are important factors in this test. The test has two parts, Coding A & Coding B.
- Coding A: this part is for subjects under 8 years or suspected mental defects. The test should be completed in 120 seconds. The score is the number of designs completed in that time. (Excluding samples) If the subject completes the test before time, bonus point is given.
- Coding B: this part is for subjects above 8 years. This section has to be completed in 120 seconds. 1 point is given for each correct response.
5. Mazes:
The test requires the subject to trace through the maze and reach the end point. The test has 5 mazes which have to be completed in the given time limit. Scoring- maze A, B, C are given 2 points if solved without error. 1 point if completed with 2 errors. Mazes 1-5 are given 3 point without error, 2 points if one error is committed, 1 point if two errors committed and 0 points when the subject passes the maximum allowed error.
Scoring of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)
For scoring the test, the raw score of all the subtests are totalled and converted into the Test Quotients (TQs) by means of the ‘T table’ in the manual. After converting into TQs, the average of each group has to be added and found out separately. To obtain full-scale IQ both the Verbal & Performance test totals are added and then divided for the average. If an only verbal group of TQs are obtained they can be balanced by adding 6% of the TQs.
Point Scale – MISIC uses the concept of point scale. All the items of a given type are grouped together in the increasing order of difficulty. The point or raw score of each subtest are totalled and converted into TQs, which are actually IQs. The subtests TQs are then added and group averaged and full scale is similarly obtained.
STANDARDIZATION SAMPLE
Sample Size- for standardization purpose over 1200 children were given full individual tests during the past 6 years and over 3000 were sampled in subtest trial runs. Average of about 90 samples were used for each level including boys and girls in a ratio of 20:30. Age norms are based on a 12-month interval.
Regional Norms- For the English version, samples were taken from Nagpur, Mumbai, Shimla, Mangalore & New Delhi. For Marathi and Hindi versions, samples were taken from Nagpur alone.
Psychometric Properties of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)
- Reliability- MISIC was established with the test-retest method and yielded a Pearson’s Product Moment correlation coefficient of 0.91 for full-scale IQ result.
- Validity- MISIC established concurrent as well as congruent validity. The former was established from school ranking whereas later was obtained from an adapted version of California short-form test of Mental Maturity for the upper age level and from the good enough Draw a Man test for the lower age level. Both yielded a coefficient of 0.63
- Norms- Indian norms are based on percentile points which were converted into IQs by Thomson formula. Using this formula anchor IQs were obtained on the basis of the standard deviation of 15 IQ.
When the IQs were plotted it gave a platykurtic graph skewed to the right. To make the graph normal two modifications were made; hypothetical 5% was added to the lower second and third standard deviation and some other modifications were made at the other extreme too. Most of the raw score fell under 16th percentile to 84th percentile; this made the 95th percentile a very high scoring norm. The abnormality of the graph was found to be due to 2 reasons; lack of subnormal cases and lack of extra normal cases.
Applications of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)
- Used as a tool in the educational setting as well as clinical setting.
- Helps teachers and parents in guiding students for educational and vocational planning.
- Used to diagnose learning disabilities in students.
- To identify children with ADHD problem
- Used to identify talented and gifted students, and also mentally challenged students.
- Used in identifying students cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
- Used in tracking intellectual development.
A sample report Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)
Purpose– To assess the intelligence of subject with help of Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)
introduction —
Informed consent:
The participant was initially given a brief description of the test. They were informed that their participation was entirely voluntary, allowing them to decline if it was inconvenient. A consent form was provided, and all relevant details were explained before soliciting their signature
Informed consent form
This form seeks your consent to participate in the study. The following information will help you decide whether to participate or not. If you agree, you’re free to withdraw at any point during the experiment. All provided information will remain confidential and unassociated with your name. Should you feel uncomfortable at any stage, you may leave, and your information will be discarded. Upon completion, you can request the experiment’s results and ask any questions. Please indicate your understanding and agreement by signing below. Your participation is voluntary, and all data will remain confidential.
Applicant’s Name: XYZ
Signature of the Applicant (Parent):
Rapport Formation:
Before giving instructions, a rapport was established by providing the participant with a brief overview of the study. Ensuring comprehension, the details were explained in the participant’s preferred language. Arrangements for the experiment were made appropriately, addressing any concerns the participant had to ensure smooth conduction.
Material
Manual, stationary
Demographic Details:
– Name: Xyz
– Age: 16
– Gender: Male
Instructions:
1. Information Test: Questions on factual knowledge of people, places, and common phenomena.
2. General Comprehension Test: Questions on practices and behavior in certain situations.
3. Arithmetic Test: Questions based on simple mental mathematical calculations.
4. Analogy & Similarity Test: Questions to find similarities between two things.
5. Vocabulary Test: Measures general intelligence.
6. Digit Span Test: Repeat sets of numbers in the same/reverse sequence.
Procedure:
To establish rapport, the tester introduced herself, explained the test and its procedures, ensuring the participant’s freedom to opt-in or out at any time, even after testing commenced. Subsequently, test instructions were given.
Precautions:
1. Ensured adequate environmental conditions for the subject’s comfort.
2. Concealed relevant materials until required.
3. Kept the purpose of the test undisclosed even after administration.
4. Provided support for ease and accurate responses.
5. Read instructions thoroughly and encouraged clarification.
6. Quietly observed the subject during testing.
7. Inquired about any past/present psychiatric illness or drug intake from the subject.
Results:
| TESTS | RAW SCORES | TQ SCORE |
|---|---|---|
| Information Test | 16 | 83 |
| General Comprehension Test | 28 | 160 |
| Arithmetic Test | 18 | 144 |
| Analogy And Similarity Test | 18 | 115 |
| Vocabulary Test | 40 | 95 |
| Digit Span Test | 13 | 115 |
VQ (Verbal Quotient) = Total TQ/6 = 118.6
Interpretation And Discussion:
The verbal scales reflect the child’s ability with abstract symbols, benefit from education, verbal memory, and fluency. The verbal IQ was 118, indicating above-average verbal intelligence.
– Information Test (16, 83): Indicates dull normal verbal ability and intellectual curiosity.
– General Comprehension Test (28, 160): Indicates very superior social judgment and understanding.
– Arithmetic Test (18, 115): Indicates above-average numerical reasoning.
– Similarities and Analogies Test (18, 115): Indicates above-average abstract intelligence and verbal reasoning.
– Vocabulary Test (40, 95): Indicates above-average language usage and verbal fluency.
– Digit Span Test (13,115): Indicates above-average ability in remembering numbers.
If you want to buy MISIC, Please mail us on careershodh@gmail.com
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,420 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2019, April 13). Malins Intelligence Scale for Indian Children (MISIC)- Master the 2 Domains of the Scale. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/malins-intelligence-scale-for-indian-children/

How can I get this test
It is quite hard to get it because most of the recent agencies don’t have this test with them. The original publisher might have stopped the publication. Try to get another one.
My daughter had taken this test at AIIMS New Delhi. Or you can check with a Psychologist they may be able to help you.
contact to psycho prasad corporation. they sale all psychology tests
I Have some 17-18 years student. Can I do MISIC on these children? If ye, Please suggest me how I will Calculate Actual age with mental age.
yes, you can do. take 15 years age for chronical age ..
but most of the clinician prefer to use Binet kamath intelligent test for above the 15 years children.
No age range is only 6 to 15.11
Pls send about test process of MISIC
It has the same process as WAPIS. Check it once.
What abilities are actually shown by the eleven sub test?
Please advise where can we order MISIC? if it is not availabe which other IQ test is standardized and suitable for Indian children?
Please advise
It is with us. Please send Your Requirements on careershodh@gmail.com
I have a doubt in this test as described above it have 12 subtest divided into 2 as verbal 6 and in performance 5 but we can only see 11 subtest how it is divided as 12
Yes, there are 6 verbal tests and 5 performance test so in total there are 11 subtests only in MISIC.
Do you have a complete set of MISIC. All scales?
Yes. Please send us an email on careershodh@gmail.com
What are the limitations of this test
Hello sir
What is the cost of Malin’s intelligence test ?
Please mail us on careershodh@gmail.com for more details.
Hello Sir/Madam,
How can one interpret the scores obtained by a child for Mailn’s test. What is the range for low, average, above average for each of the test.
Regards,
Harish