Introduction
When a child is not performing well in school, he/she is usually labeled with different names. In fact, we must try to find the root cause behind their inability. Certain Learning Disabilities Test will help us understand that there are biological or environmental factors affecting the child’s inability.
If you are a parent or a teacher and you know a child who is unable or faces difficulty in doing the following, then you must consider approaching a professional.
- Difficulty in reading
- Jumbles letters in writing
- Low spatial intelligence
- Finds simple arithmetic sums hard to solve
Children who do not learn at a normal rate for reasons other than general mental impairment, lack of opportunity, social-emotional disturbance, or sensory defect are referred to as learning disabled.
An expert in educational psychology conducts tests to diagnose whether someone has a learning disability or not.
A professional carries out Behavioral Observation by –
- Direct Observation
- Role Play
- Self Report
According to most estimates, between 5-15 per cent of school aged children have learning disability.
As per the law of Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), providing proper diagnosis and remedial guidance to people with learning disabilities is compulsory.
Types of Learning Disabilities
General –
- Speech and Language
- Temporal Relationships
- Auditory and Visual Perception
- Quantitative Reasoning and Computational Skills
- Motor Skills
Specific Learning Disabilities (SLD) –
- Dyslexia
- Dysgraphia
- Dyscalculia
Tests for Learning Disabilities
1. NIMHANS Index for Specific Learning Disabilities
This battery of tests was originally developed by John (1989). The test was standardized in a population of 50 children with learning disability and 50 normal children.
In 1992 Kapur and associates (Kapur et al, 1992) expanded this test.
Now it consists of the following tests:
- Attention Test (Number Cancellation)
- Language Test (Reading, Writing, Spelling and Comprehension)
- Arithmetic Test (Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, and Fractions)
- Visuo-motor Skills (The Bender Gestalt Test and Developmental Test of Visuo-motor Integration)
- Memory (Auditory and Visual).
The scale was administered to children from slum schools as well as those catering to the middle class.
NIMHANS Index for Specific Learning Disabilities has two levels: Level I and Level II.
The first is meant for children in the age group of 5-7 years and the second, for those who are in classes 1-7.
2. Diagnostic Test of Learning Disabilities
Swarup and Mehta, (1991) developed this diagnostic test of learning disability. The test consists of 100 items in 8 different core areas, which includes –
- Visual processing
- Auditory processing
- Motor-coordination
- Cognitive
- Language
- Memory functions
- Perseverence tendencies and disorders
Assessment is conducted in different areas of functioning such as-
- EyeHand Coordination (EHC)
- Figure-Ground Perception (FG)
- Figure Constancy (FC)
- Position in Space (PS)
- Spatial Relations (SR)
- Auditory Perception (AP)
- Cognitive Abilities (CA)
- Memory (M)
- Receptive Language (RL)
- Expressive Language (EL)
3. Reading Disability Tests
Woodcock Reading Tests
There are five subtests in Woodcock Reading Tests-Revised/Normative Update
(WRMT-R/NU) (Woodcock, 1998).
They include
- Letter identification (naming different uppercase and lower case manuscripts and cursive letters of the alphabet)
- Word identification ( identification of specific words)
- Word attack ( identification of nonsense words)
- Word comprehension (completion of analogy formats)
- Passage comprehension (silent reading of a passage and supplying appropriate words for the blanks).
The test is used for children upto 12th grade.I
Moreover, there are other reading tests such as –
- Ekwall Reading Inventory
- Gates-McKillop-Horowitz Reading Diagnostic Tests
- Durrell Analysis of Reading Difficulty
- Diagnostic Reading Scales
4. Writing Disability Tests
1) Picture-Story Language Test
Myklebust developed this test(1965) to study written expression. A student as to see a picture and write a story on it. They evaluated the stories in terms of productivity, correctness and meaning.
2) Sequential Test of Educational Progress
Educational Testing Service developed this test(1985). This is a standardized test that consists of items in the following areas: organisation, conventions, critical thinking, effectiveness and appropriateness.
They prepared the test by analyzing the actual errors made by the students in writing.
5. Mathematics Disability Tests
There are number of other diagnostic tests of mathematics. Widest range of tests covering
KG to Grade 12 are –
- Comprehensive Test of Basic Skills
- Iowa Tests of Basic Skills
- Stanford Achievement Test
- Kaufman Test of Educational Achievement-Normative Upgrade (K-TEA-NU)
- Peabody Individualized Achievement Tests- Revised (PIAT-R)
- Stanford Diagnostic Mathematics Test (SDMT, 3rd ed.)
- Test of Early Mathematic Ability-2 (Grades Pre-school-3)
- Test of Mathematical Abilities-2 (Grades 3-12)
- Enright Diagnostic Inventory of Basic Arithmetic Skills (Grades 6-Adult)
- Diagnostic Mathematic Inventory Mathematic System (Grade 1-12)
Learning Quotient formula
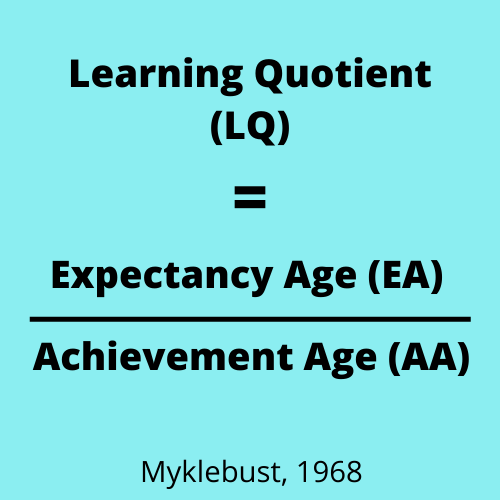
- Expectancy age (EA) = Mental Age(MA) + Chronological Age (CA) + Grade Age (GA) / 3
- Achievement age is calculated by using achievement tests.
If the score is less than 0.98 the individual as learning disabled.
References
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 15,150 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2022, July 8). Learning Disabilities: Diagnosis, Types & Tests. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/learning-disabilities-diagnosis-types-tests/
