Indian Perspectives on Sustainable Development
India, one of the fastest-growing economies and home to nearly 1.4 billion people, has emerged as a pivotal player in the pursuit of global sustainable development. With its complex socio-economic challenges and cultural diversity, India’s strategy towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is both ambitious and comprehensive.
Since the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, India has demonstrated a “whole-of-society” approach to address poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and climate change. The principles of inclusive growth and sustainable development align with the Indian government’s motto of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas” (Collective Efforts, Inclusive Growth) (United Nations, 2020).
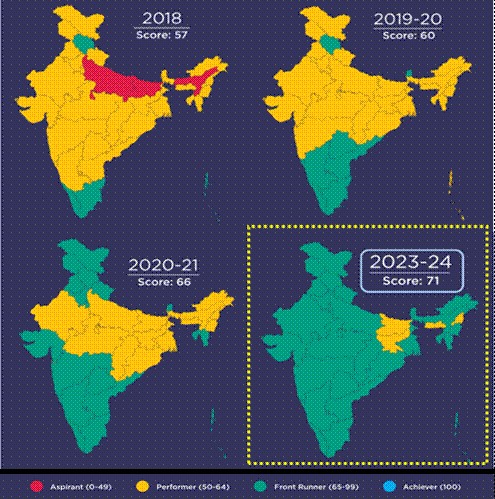
India’s SDG Score According to the GOI Retrieved from https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2032857
Poverty Alleviation and Economic Growth
India’s commitment to ending poverty in all its forms (SDG 1) is reflected through targeted economic reforms, financial inclusion programs, and rural employment schemes. Programs such as-
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) have provided over 2 billion person-days of employment annually, significantly enhancing rural infrastructure and purchasing power (Government of India, 2020). MGNREGA, often described as the world’s largest cash transfer program, has not only reduced poverty but also promoted gender equality by ensuring significant female participation.
Trends in MGNREGA Over the Years Retrieved from https://www.theindiaforum.in/article/continuing-relevance-mgnrega
- The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), launched in 2014, is another cornerstone initiative aimed at financial inclusion. PMJDY has facilitated the opening of more than 400 million bank accounts, enabling direct benefit transfers (DBT) to marginalized populations (NITI Aayog, 2020). Leveraging the Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) trinity, India has efficiently targeted subsidies and benefits, ensuring transparency and reducing leakages.
In addition, India’s economic growth trajectory remains key to its poverty alleviation strategy. With a GDP of $2.72 trillion (2019), India aims to become a $5 trillion economy by 2025 through initiatives like “Make in India” and “Digital India” (Government of India, 2020). These programs stimulate entrepreneurship, infrastructure development, and technological innovation, creating job opportunities and driving inclusive growth.
Environmental Sustainability and Climate Action
India’s commitment to environmental sustainability is evident in its climate action strategies under SDG 13. The country has made substantial progress in reducing carbon emissions, promoting clean energy, and enhancing disaster resilience. India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), as part of the Paris Agreement, aim to reduce the emissions intensity of GDP by 33-35% by 2030 compared to 2005 levels (UNFCCC, 2019).
Programs like-
- National Mission for Green India and the National Afforestation Program focus on restoring degraded ecosystems and increasing forest cover. India has set a target to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030, promoting biodiversity and sustainable land management (United Nations, 2020).
- The government has also launched the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) to address the growing impact of natural disasters and ensure infrastructure resilience.
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Mission) is another landmark initiative addressing sanitation and environmental health. Launched in 2014, the mission achieved 100% rural sanitation by constructing over 100 million toilets. This initiative significantly reduced open defecation and improved hygiene, contributing to better public health and environmental outcomes (Government of India, 2020).
Renewable Energy Transition
India has emerged as a global leader in renewable energy, aligning with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). As part of its commitment to clean energy, India has set ambitious targets, including achieving 450 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 (IEA, 2020). Presently, India ranks third in renewable power capacity, fourth in wind energy, and fifth in solar power globally.

Trends in Renewable Energy Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/02/climate-policy-india/
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA), spearheaded by India, fosters global cooperation for solar energy adoption. ISA aims to mobilize $1 trillion in investments for solar projects, particularly in developing countries, by 2030 (International Solar Alliance, 2020).
- Domestically, the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana has provided clean cooking fuel (LPG) to over 80 million poor households, reducing dependence on biomass and improving indoor air quality.
- Energy efficiency programs, such as the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) scheme and the UJALA initiative, have further contributed to reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions. The UJALA program has distributed over 360 million LED bulbs, leading to annual savings of 38 million tonnes of CO2 emissions (Government of India, 2020).
Health and Well-Being
Ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being (SDG 3) remains a priority for India. The Ayushman Bharat program, launched in 2018, is the world’s largest health protection scheme, covering over 500 million people with an annual health insurance cover of $7,000 per family (Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, 2020). This initiative addresses the financial burden of healthcare for vulnerable families while strengthening primary and tertiary healthcare infrastructure.
- The National Health Mission (NHM) and Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) have improved maternal and child health outcomes. India has witnessed a sharp decline in maternal mortality rates (MMR) and infant mortality rates (IMR) over the past decade. Immunization programs, such as Mission Indradhanush, aim to achieve full vaccination coverage for all children under five years of age.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, India demonstrated remarkable resilience through initiatives like the SAARC COVID-19 Emergency Fund and domestic economic stimulus packages worth $22.5 billion. India also emerged as a key supplier of COVID-19 vaccines, supporting global efforts to combat the pandemic (World Health Organization, 2021).
Education and Social Inclusion
Education is central to India’s sustainable development agenda, aligning with SDG 4 (Quality Education). The Right to Education Act (2009) mandates free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14 years, ensuring equitable access to quality education. Programs such as-
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the Mid-Day Meal Scheme have enhanced school enrollment and reduced dropout rates, particularly among disadvantaged communities (NITI Aayog, 2020).
- Higher education reforms, including the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, focus on fostering critical thinking, innovation, and skill development. The NEP emphasizes inclusive and equitable education, bridging gaps in access for girls, rural populations, and marginalized groups.
Financial inclusion through initiatives like the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (Save the Girl Child, Educate the Girl Child) program has empowered women and girls, promoting gender equality (SDG 5). The program combines awareness campaigns, financial incentives, and education support to address gender disparities.
Global Partnerships for Sustainable Development
India’s role in fostering global partnerships aligns with SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals). Through South-South Cooperation, India supports developing nations with financial assistance, capacity-building programs, and technical expertise.
- The India-UN Development Partnership Fund, established in 2017, has funded projects in over 50 countries, addressing poverty, climate resilience, and infrastructure development (United Nations, 2020).
India’s leadership in initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance and the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure reflects its commitment to global sustainable development. Additionally, India’s advocacy for climate justice highlights the principle of “common but differentiated responsibilities,” emphasizing the need for developed nations to support climate mitigation efforts in developing economies (UNFCCC, 2019).

SDG India Index 2023-24
Challenges in Achieving the SDGs
Despite significant progress, India faces challenges in achieving all 17 SDGs. The key challenges include-
- Income Inequality- While economic growth has reduced poverty, disparities in wealth and income distribution persist. Marginalized communities, including women, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes, remain disproportionately affected.
- Urbanization- Rapid urbanization has led to challenges such as overcrowding, inadequate infrastructure, pollution, and housing shortages. Sustainable urban development requires integrated planning and investment.
- Environmental Degradation- Issues like deforestation, land degradation, water scarcity, and pollution continue to threaten India’s natural resources. Robust environmental policies and conservation efforts are essential.
- Resource Constraints- Financing sustainable development remains a critical priority. India requires significant investments to meet SDG targets, particularly in infrastructure, health, and education.
- Implementation Gaps- While policies exist, gaps in implementation, monitoring, and accountability hinder progress. Strengthening governance frameworks is crucial.
- Technological Integration- Leveraging technology for sustainable solutions is essential, but digital divides and lack of infrastructure in rural areas pose challenges.
- Localizing SDGs- Addressing region-specific challenges through cooperative federalism and SDG localization at the state and district levels remains a priority.
- Grassroots Participation- Encouraging business sustainability practices, civil society involvement, and grassroots movements is vital for achieving inclusive progress.
Conclusion
India’s approach to sustainable development is a holistic blend of economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental sustainability. Through bold initiatives like the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Ayushman Bharat, and renewable energy programs, India has demonstrated its leadership in addressing global challenges. While the road to achieving all SDGs remains challenging, India’s commitment to inclusive growth and climate action offers a blueprint for sustainable development. By fostering innovation, strengthening partnerships, and empowering marginalized communities, India is poised to contribute significantly to a sustainable and equitable future for all.
References
Government of India. (2020). Sustainable Development Goals: India’s progress and initiatives. Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
International Energy Agency (IEA). (2020). India 2020: Energy Policy Review. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/india-2020
International Solar Alliance. (2020). Scaling solar energy solutions for a sustainable future. Retrieved from https://isolaralliance.org
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. (2020). Ayushman Bharat: National Health Protection Scheme. Government of India.
NITI Aayog. (2020). SDG India Index: Baseline report. Retrieved from https://niti.gov.in
United Nations. (2020). India and the Sustainable Development Goals. Retrieved from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/memberstates/india
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). (2019). India’s Nationally Determined Contributions. Retrieved from https://unfccc.int
World Health Organization. (2021). India’s COVID-19 response and vaccine distribution. Retrieved from https://www.who.int
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,557 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2024, December 19). Indian Perspectives on Sustainable Development and 8 Important Challanges. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/indian-perspectives-on-sustainable-development/
