Introduction to Herzberg two factor theory
Herzberg two factor theory is a significant framework in business management that delineates the factors affecting employee motivation and job satisfaction. The theory identifies two distinct categories: motivation factors and hygiene factors. Motivation factors, such as achievement and recognition, inspire and engage employees, whereas hygiene factors, including salary and working conditions, are essential to prevent dissatisfaction. The interplay of these factors can significantly influence an employee’s overall job satisfaction and engagement. High levels of both hygiene and motivation contribute to maximum employee engagement, while low levels in either category can lead to dissatisfaction and high turnover rates.
Highlights of Herzberg two factor theory
- Motivation vs. Hygiene Factors: Herzberg’s theory distinguishes between motivators that inspire employees and hygiene factors that prevent dissatisfaction.
- Impact on Job Satisfaction: Both hygiene and motivation factors play crucial roles in shaping overall job satisfaction.
- Importance of Compensation: Adequate salary and benefits are vital hygiene factors that can significantly influence employee morale.
- Work Environment Matters: Comfortable working conditions are essential; poor conditions can lead to dissatisfaction, regardless of motivation levels.
- Engagement Levels: The right combination of hygiene and motivation factors can lead to high employee engagement and productivity.
- Turnover Risks: Low levels in either hygiene or motivation can increase employee turnover and dissatisfaction.
- Managerial Implications: Managers must ensure both hygiene factors and motivators are adequately addressed to foster a motivated workforce.
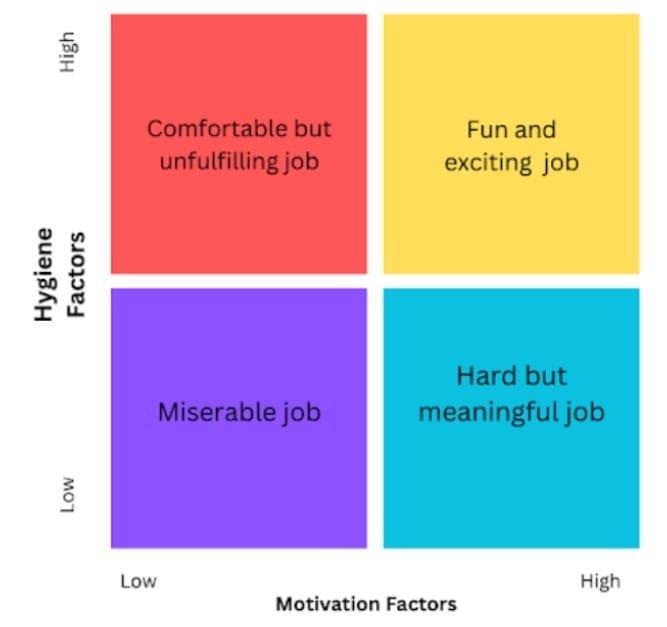
Motivators and hygiene factors combinations in Herzberg’s two-factor theory
Herbzerg’s theory suggests that there are two types of factors that affect employee satisfaction and motivation: hygiene factors and motivators. When employees have high levels of both hygiene factors and motivators, they are more likely to be highly engaged and motivated in their work. On the other hand, when employees have low levels of hygiene factors and motivators, they may experience low motivation, high dissatisfaction, and turnover. Let’s look at combinations of motivators and hygiene factors:
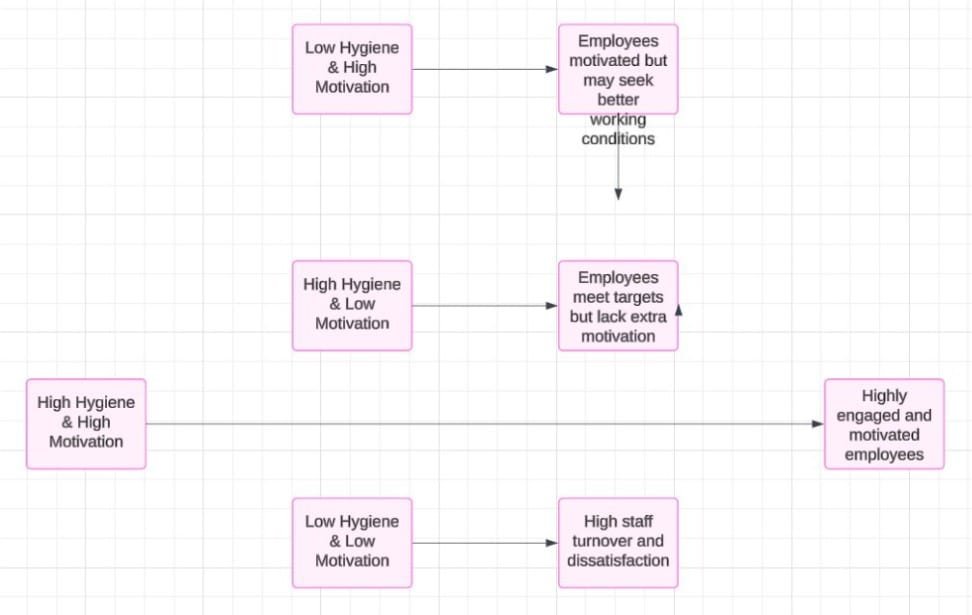
Hygiene & motivator factors
Empirical studies on job satisfaction in nurses, such as those by Kacel et al. (2005) and Jones (2011), support Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory, suggesting that motivational factors are more important for job satisfaction than hygiene factors. Kacel et al. (2005) used this theory to study job satisfaction among 147 nurse practitioners in the U.S. Midwest. They found that nurses often become nurse practitioners due to dissatisfaction with staff nursing roles and a desire for greater challenge and autonomy, which align with Herzberg’s motivational factors. The researchers created the Misener Nurse Practitioner Job Satisfaction Scale to assess factors such as collegiality, autonomy, professional growth, and salary. Their findings indicated that salary and administrative policies were key factors influencing job dissatisfaction among nurses.
| Advantages of Herzberg’s two-factor theory | Disadvantages of Herzberg’s two-factor theory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
According to Herzberg’s two-factor theory, which factor would motivate individuals the most?
- According to Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, the “motivators” are the most potent in driving job satisfaction and motivation.
- These include intrinsic aspects such as achievement, recognition, work, responsibility, advancement, and growth opportunities.
- Herzberg suggests these factors promote higher performance as they fulfil individuals’ deep-seated needs for personal growth and self-fulfilment.
- However, the exact factor motivating most would vary based on the individual’s values and needs.
Conclusion
Herzberg’s two-factor theory provides a valuable framework for understanding employee motivation and satisfaction. By recognizing the importance of both hygiene and motivation factors, organizations can create a work environment that not only attracts talent but also retains and engages employees for long-term success. Managers play a crucial role in implementing this theory through targeted strategies that address the needs and aspirations of their teams, ultimately leading to a more satisfied and productive workforce.
References
- Herzberg Two factor Theory: Business | StudySmarter. (n.d.). StudySmarter UK. https://www.studysmarter.co.uk/explanations/business-studies/human-resources/herzberg-two-factor-theory/
- Simply Psychology. (2023, September 28). Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation-Hygiene. https://www.simplypsychology.org/herzbergs-two-factor-theory.html#What-Is-Two-Factor-Theory
- Kacel, B., Miller, M., & Norris, D. (2005). Measurement of nurse practitioner job satisfaction in a Midwestern state. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners, 17(1), 27-32.
- Herz. diagram | Lucidchart. (n.d.). https://lucid.app/lucidchart/5a835ceb-2be8-4da3-ac00-a97b2aec0330/edit?viewport_loc=829%2C1141%2C2067%2C933%2C0_0&invitationId=inv_efe185ae-4707-49f2-b435-086e8d5371dc
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 14,001 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, February 8). Herzberg Two Factor Theory of Motivation. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/herzberg-two-factor-theory-of-motivation/
