HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY
Syllabus wef 2023
(EP: 450- Major Elective)
(Credits-4)
DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY
S. P. PUNE UNIVERSITY, PUNE
SEMESTER-IV
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
To acquaint students with:
1. The theoretical foundations of health psychology.
2. The role of psychological factors in health, illness, and healthcare.
3. The understanding of health promotions and interventions.
4. Application of psychological principles to promote health and manage illness.
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Students will be able to:
1. Demonstrate knowledge of key concepts and theories in health psychology.
2. Critically assess the psychological factors that influence health and illness.
3. Acquire the theoretical knowledge as interventions in chronic health problems.
4. Apply research methods to investigate health psychology phenomena.
1.0. INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY [15]
1.1. Definition, Scope, and Importance of Health Psychology
1.2. Biopsychosocial Model & Biomedical Model
1.3. Psychology’s Role in Health – Problems in the Health Care System, ‘The Person’ in
Health and Illness, How the Role of Psychology Emerged
1.4. Application: The Need of Health Psychology- Changing Patterns of Illness, Expanded Health Care Services, Increased Medical Acceptance
2.0. PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS [15]
2.1 Stress: Theories and Measurements
2.2. Coping Mechanisms and Health Outcomes
2.3. Patient Provider relationship and Communication
2.4. Psychoneuroimmunology: Interactions between Psychological Processes & the Immune
System
3.0. HEALTH BEHAVIOR CHANGE AND PROMOTION [15]
3.1. Theories of Health Behavior Change: Health Belief Model, Theory of Planned Behavior, and Transtheoretical Model
3.2. Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Programs
3.3. Risk Behaviors and Health: Smoking, Alcohol, and Substance Abuse
3.4. Interventions to Promote Healthy Lifestyles: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, Rest, Vaccination and Screening, Accident prevention
4.0. CHRONIC ILLNESS AND PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVENTIONS [15]
4.1. Psychological Impact of Chronic Illness: Cancer, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases
4.2. Pain Management and Psychological Approaches
4.3. Developmental, Gender, and Sociocultural Factors in Health-Development and Health
4.4. Health Promotions
Books for Readings
- Aronson, E., Wilson, T. D., & Akert, R. M. (2019). Health Psychology (10th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
- Biddle, S. H., & Fox, C. R. (2004). The Psychology of Physical Activity (4th ed.). Routledge.
- Brannon, L., & Feist, J. (2017). Health Psychology: An Introduction to Behavior and Health (9th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Goldberger, L. F. (Ed.). (2012). The Oxford Handbook of Stress, Health, and Coping. Oxford University Press.
- Greenberg, D. S., Caliares, R. F., Hyman, S. M., & Murphy, S. L. P. (2019). Behavioral Medicine: Integrating Physical and Behavioral Science (7th ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
- Hogg, M. (Ed.). (2013). The Handbook of Health Psychology (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Marks, D. F., & Murray, M. (2013). Positive Health Psychology (2nd ed.). Open University Press.
- McEwen, B. S. (2017). Stress and Health (8th ed.). Psychology Press.
- Ogden, J. (2017). Health psychology: A textbook (4th ed.). McGraw Hill Education.
- Sarafino, E. P., & Smith, T. W. (2020). Health Psychology: Biopsychosocial Interactions (10th ed.). Wiley.
- Schneiderman, N., Spielberger, C. D., & Strelau, J. (Eds.). (2025). APA Handbook of Health Psychology.
- Straub, R. O. (2019). Health Psychology: A Biopsychosocial Approach (5th ed.). Worth Publishers.
- Taylor, S. E. (2011). The Social Psychology of Health: Outcomes and Interventions (2nd ed.). Psychology Press.
- Taylor, S. E. (2018). Health Psychology (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
- Waitz, J. P., & Lloyd, S. M. (2016). An Introduction to Health Psychology (8th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
- Weiten, W. and Lloyd, M. (2007). Psychology applied to modern life: Adjustment in the 21st century, Indian Edition 8th. Thomson
FAQs About Health Psychology
1. What is health psychology?
Health psychology is a field of psychology that focuses on how biological, psychological, and social factors influence health and illness. It aims to promote health, prevent diseases, and improve healthcare systems.

2. How does health psychology differ from clinical psychology?
While clinical psychology primarily deals with diagnosing and treating mental health disorders, health psychology focuses on how psychological factors affect physical health and how to encourage healthier behaviors.
3. What are some key topics studied in health psychology?
Health psychologists study areas such as stress and its effects on health, health behavior change (e.g., quitting smoking, exercising), coping with chronic illnesses, pain management, and the impact of psychological factors on medical conditions.
4. How can health psychology help improve overall well-being?
It helps by identifying behaviors that affect health (e.g., poor diet, lack of exercise), designing interventions to promote healthier habits, and assisting patients in managing chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease.
5. What role does stress play in health psychology?
Stress is a major focus in health psychology because it can contribute to physical conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and weakened immunity. Health psychologists help people develop stress management strategies to reduce these risks.
6. How do health psychologists promote behavior change?
They use various techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, and health education to encourage healthier behaviors like regular exercise, better eating habits, and medication adherence.

Factor Influencing Health Behavior
7. Where do health psychologists work?
Health psychologists work in hospitals, clinics, universities, research institutions, public health organizations, and private practices. They may also collaborate with medical professionals to improve patient care.
8. Can health psychology help with chronic illness management?
Yes, health psychologists assist individuals in coping with chronic illnesses like diabetes, cancer, and hypertension by helping them adjust their lifestyle, manage stress, and adhere to treatment plans.
9. What is the biopsychosocial model in health psychology?
The biopsychosocial model is a framework that explains health and illness as the result of interactions between biological (genetics, physiology), psychological (thoughts, emotions), and social (environment, culture) factors.
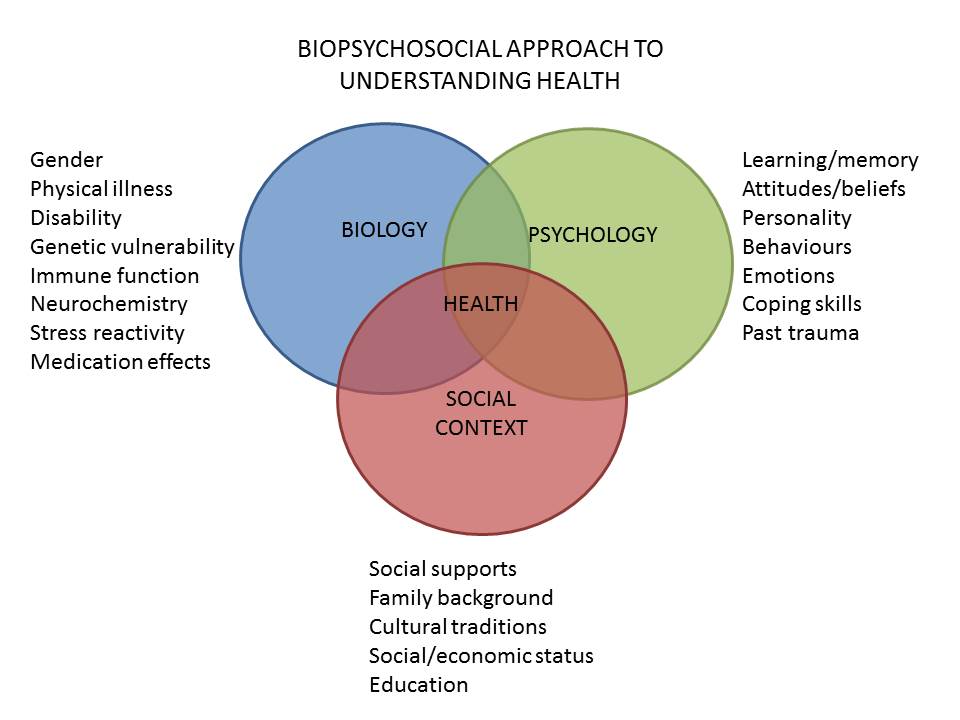
Biopsychosocial Model of Health
10. How does health psychology contribute to public health?
Health psychologists work on designing public health campaigns, researching health behaviors, and developing policies that encourage healthier lifestyles to reduce the burden of diseases on society.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 14,002 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, March 12). Health Psychology Notes. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/health-psychology-sppu-syllabus/
