What is Group Dynamics?
Group dynamics is a term used to describe the interaction and processes of a group. For sports, knowing these dynamics can be vital for maximizing team performance and individual health. Some of the most important areas of group dynamics are:
Group Formation:
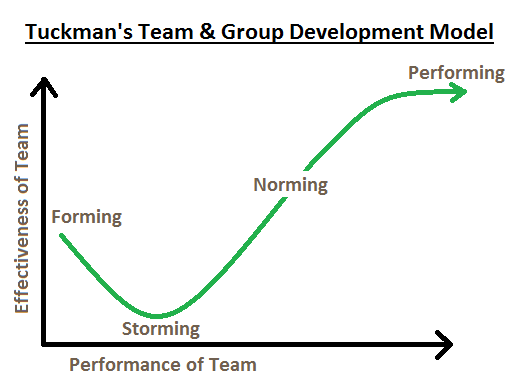
Tuckman’s stages of group development (Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, Adjourning) are used to create a model for the manner in which teams develop.
- Forming: Starting stage with ambiguity and reliance. Members become acquainted with one another and form initial perceptions.
- Storming: Strife arises when members establish themselves and challenge direction. This can be a seminal phase for defining team identity but must be approached cautiously.
- Norming: Team defines rules, norms, and expectations. Team cohesion starts as members establish where they fit on the team.
- Performing: The team functions well towards common objectives. Roles are well defined, and members are very motivated.
- Adjourning: The team breaks up after it has accomplished its objectives or at the end of a season. This phase may include feelings of loss and needs proper closure.
© Emma-Louise. (2024, July 8). The Coaching Tools Company.
Factors influencing Group Dynamics
- Roles and Responsibilities: Members of a sports team play distinct roles (e.g., captain, playmaker, defender). Well-defined roles and responsibilities are crucial to successful collaboration and development of conflict. Knowledge of one’s role is a factor in an individual’s satisfaction and team success.
- Patterns of Communication: Coordination of activities, conflict resolution, and the establishment of trust depend on effective communication. Communication can either be verbal or non-verbal, and team performance is greatly influenced by its quality. Patterns of communication can help detect problems like information overload, misunderstandings, or absence of feedback.
- Leadership: The team captain’s or coach’s leadership style has a great impact on group dynamics. Various leadership styles (e.g., autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire) will have different impacts on team morale, motivation, and performance. Successful leaders modify their style to suit the particular needs of the team and situation.
- Conflict and Conflict Management: Conflict is unavoidable in any group. It’s essential to have plans for handling and resolving conflict positively. Overlooking conflict might give rise to resentment and lowered performance, but resolving it effectively can enhance team cohesion. Conflict management plans could be negotiation, mediation, or compromise.
- Team Culture: This is the common values, beliefs, and norms that define a team. A positive team culture builds a sense of belonging, inspires motivation, and improves performance. Team culture is usually determined by leadership, team history, and shared experience.
Group Cohesion
Group cohesion is the changing process that illustrates the tendency for a group to remain together and stay united in the pursuit of its instrumental goals and/or the fulfillment of affective member needs. It’s the “glue” that keeps a team together. Two critical dimensions of cohesion are:
- Task Cohesion: The extent to which members are dedicated to the team’s goals and objectives. This indicates a common wish to succeed.
- Social Cohesion: The extent to which members enjoy each other’s company and like being together. This indicates the interpersonal attraction and friendship within the team.
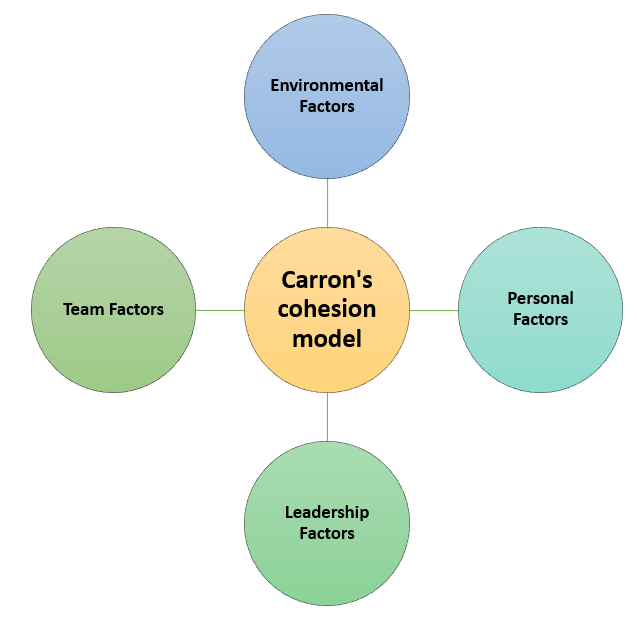
Carron’s cohesion model
It outlines four important antecedents:
- Environmental Factors: Situational conditions like team size, degree of competition, and members’ proximity.
- Personal Factors: Personal traits of team members such as their motivation, satisfaction, and similarity with other members.
- Leadership Factors: The captain or coach’s style and behavior, including communication, decision-making, and motivational styles.
- Team Factors: Those aspects related to the team itself, i.e., history, success, and common purpose.
Advantages of Cohesion:
- Enhanced Performance: Cohesive teams perform better than less cohesive teams, particularly in team sports.
- Higher Adherence: Team members are more likely to show up for practices and training sessions.
- Increased Motivation: Cohesion can enhance individual motivation and effort.
- Higher Satisfaction: Team members in cohesive teams typically report higher satisfaction and enjoyment.
- Less Conflict: Cohesion has the ability to reduce conflict and enhance positive relationships.
- Greater Resilience: Cohesive teams are more resilient to challenges and setbacks.
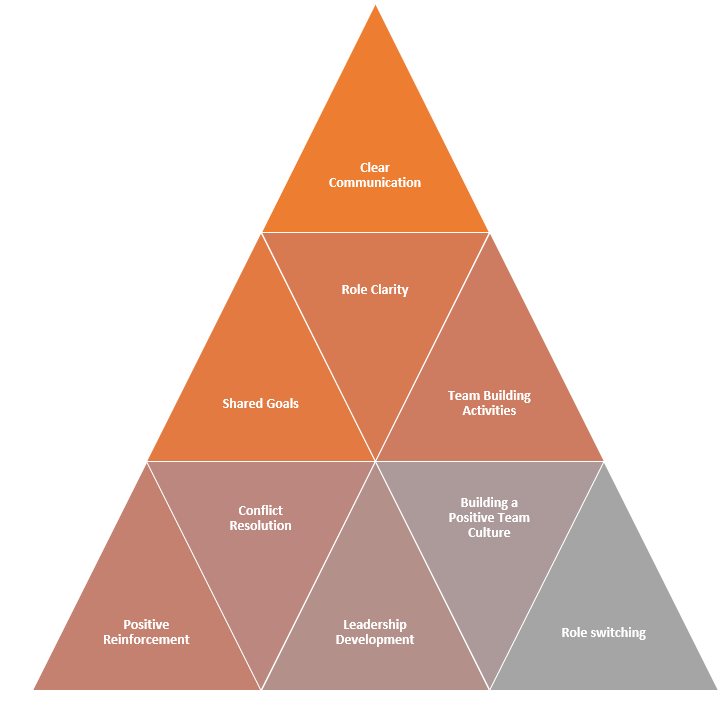
Strategies for Cohesion Building:
- Clear Communication: Encourage open and honest communication between team members.
- Shared Goals: Set clear and challenging team goals that all members are committed to.
- Role Clarity: Make sure each member knows their role and responsibilities.
- Team Building Activities: Participate in activities that encourage interaction and cooperation.
- Positive Reinforcement: Give encouragement and praise for individual and team achievements.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolve conflict constructively and early.
- Leadership Development: Develop leaders through effective communication and team-building capabilities.
- Building a Positive Team Culture: Establish a positive and supportive team culture in which all individuals feel valued.
Relation Between Group Dynamics and Cohesion:
Group dynamics is the basis from which teams and their operation can be understood, whereas cohesion defines the quality or intensity of connections in the team. Positive group dynamics with well-functioning communication, clear definition of roles, and resolution of conflict are integral to creating robust team cohesion. Issues with group dynamics, i.e., ineffectiveness of communication or pending conflict, serve to hamper cohesion building.
Conclusion
It is important for coaches, athletes, and all participants in team sports to understand group dynamics and group cohesion. By creating positive group dynamics and establishing good team cohesion, it is possible to improve performance, individual well-being, and the enjoyment and satisfaction of the sporting experience. Keep in mind that these are dynamic processes that need constant attention and effort.
References
- Cox, R. (2006). Sport Psychology. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Emma-Louise. (2024, July 8). The 5 Stages of Tuckman’s Team and Group Development Model Plus How to use it | by Emma-Louise. The Coaching Tools Company.
- Jarvis Matt (2006). Sport Psychology : A student’s Handbook. Routledge.
- Weinberg, R. S., & Gould, D. (2019). Foundations of Sport and Exercise Psychology (7th ed.). Human Kinetics.
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, March 24). Group dynamics & Group Cohesion in Sports. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/group-dynamics-group-cohesion-in-sports/
