Introduction
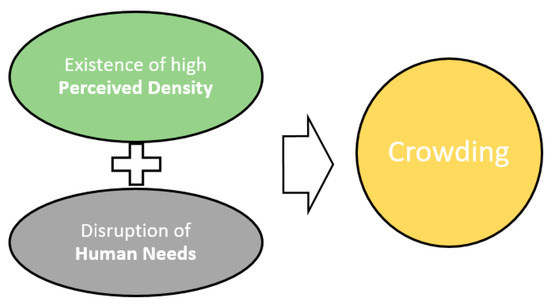
Crowding is a psychological condition that arises when the demand for space exceeds the availability, leading to stress, frustration, and even aggression. While it is often a result of high density, it is not synonymous with it. Fortunately, there are evidence-based strategies to reduce or eliminate both the causes and effects of it through thoughtful design, behavioral interventions, and policy measures.
Read More- Noise and Its Effects on Animals and Humans
Core Causes of Crowding
- Physical Design Flaws: Poor layout, narrow corridors, and inadequate exits all amplify perceived.
- Lack of Control: When individuals feel trapped or unable to adjust their environment, psychological discomfort increases (Evans & Cohen, 1987).
- Noise and Sensory Overload: Excessive noise, heat, and lighting can make a space feel more crowded than it is (Basner et al., 2014).
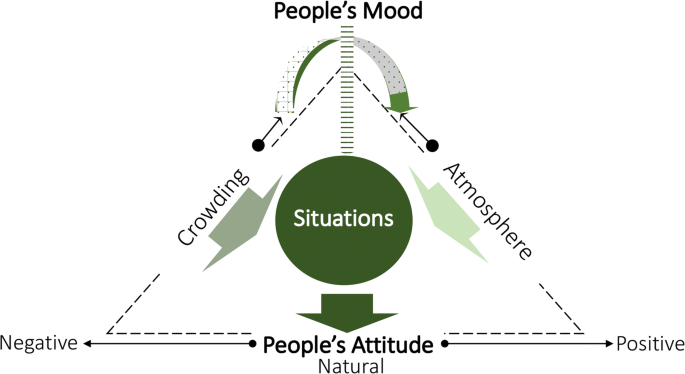
- Social Density: When social expectations are violated—such as in elevators or crowded buses—people experience psychological crowding.
Factors Affecting Crowding
Effects of Crowding
- Stress and Burnout: Constant exposure to crowded conditions can cause chronic fatigue and emotional distress.
- Aggression and Conflict: Studies show a correlation between it and higher incidences of violence in residential and correctional settings.
- Reduced Productivity: Crowded classrooms and offices hinder concentration and performance.
Mood
Eliminating Causes: Design and Architecture
Some of the causes include-
- Open and Flexible Layouts: Spaces that feel open reduce visual and physical crowding.
- Green Spaces: Natural elements, even indoors, help restore attention and reduce stress (Kaplan & Kaplan, 1989).
- Acoustic Design: Reducing noise with proper materials and layout reduces sensory overload.
Density
Behavioral and Policy Interventions
- Urban Planning: Zoning regulations can control residential density and prevent overcrowding.
- Public Transport: Increasing capacity and frequency can reduce commuter crowding.
- Workplace Flexibility: Hybrid work models reduce office density and increase well-being.
Conclusion
It is a multifaceted problem that goes beyond physical numbers. It involves perception, control, and environment. Through smart design and conscious policy, we can create spaces that enhance well-being, reduce stress, and support sustainable living.
References
Evans, G. W., & Cohen, S. (1987). Environmental stress. In Handbook of Environmental Psychology.
Kaplan, R., & Kaplan, S. (1989). The Experience of Nature. Cambridge University Press.
Basner, M., et al. (2014). Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. The Lancet, 383(9925), 1325–1332.
Gifford, R. (2007). Environmental Psychology: Principles and Practice.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,619 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, April 24). 4 Important Causes of Crowding and How to Eliminate It. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/crowding/
