Biofeedback and neurofeedback are methods that enable individuals to attain awareness and control over physiological functions that are usually automatic. In athletics, these methods are utilized to improve performance through the optimization of physiological and neurological conditions.
Biofeedback:
Biofeedback consists of tracking physiological signals (e. g. , heart rate, muscle tension, skin conductance) and offering immediate feedback to the person. This enables them to gain control over these signals.
As Cox (2006) highlights, biofeedback is a technique that gives athletes insight into their physiological reactions, allowing them to cultivate self-regulation abilities.
Physiological Measures:
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV): Assesses the variation in time intervals between heartbeats. Elevated HRV is commonly linked to enhanced adaptability and resilience, which is advantageous for athletes.
- Muscle Tension (EMG): Electromyography (EMG) assesses muscle activity. Athletes can understand how to minimize unnecessary muscle tension, resulting in more efficient movement and lower injury risks.
- Skin Conductance (GSR): Galvanic skin response (GSR) evaluates changes in sweat gland activity, indicating arousal levels. Athletes can learn to regulate their arousal to optimal levels for performance.
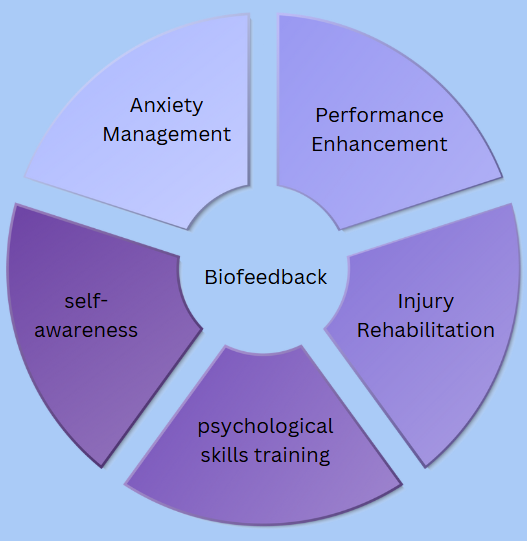
Applications in Sports:
- Anxiety Management: By managing their heart rate and muscle tension, athletes can utilize biofeedback to alleviate anxiety both before and during competition.
- Performance Enhancement: Athletes can enhance focus, concentration, and reaction time by fine-tuning their arousal levels.
- Injury Rehabilitation: Biofeedback can assist athletes in recovering muscle control and alleviating pain throughout the rehabilitation process.
- Weinberg and Gould (2019) would advocate for employing biofeedback for managing anxiety and enhancing performance, as they highlight the significance of psychological skills training, which includes biofeedback.
- Matt Jarvis (2006) would endorse the use of biofeedback as a technique for athletes to develop greater self-awareness of their bodies, thus enabling them to manage their physical state.
Neurofeedback:
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback that concentrates particularly on brain function. It employs electroencephalography (EEG) to track brainwaves and deliver immediate feedback.
It allows athletes to acquire the ability to control their brainwave patterns, which can affect cognitive and emotional conditions.
Brainwave Patterns:
- Theta Waves: Linked to relaxation and sleepiness.
- Alpha Waves: Linked to relaxation and a serene, attentive state.
- Beta Waves: Linked to alertness and focus.
- SMR (Sensorimotor Rhythm): Linked to physical calmness and mental concentration.
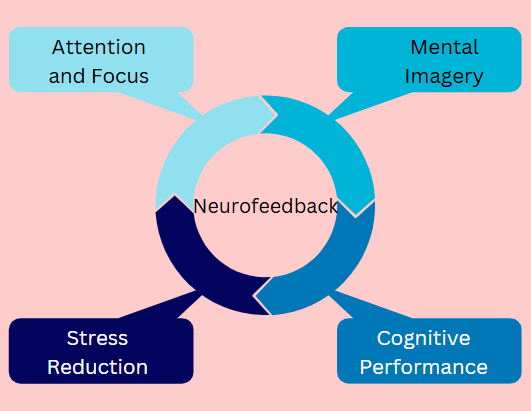
Applications in Sports:
- Attention and Focus: Athletes have the ability to train to boost beta and SMR activity, thus enhancing concentration and focus during competitions.
- Mental Imagery: Neurofeedback can improve the efficacy of mental imagery by refining brain states linked to visualization.
- Stress Reduction: By elevating alpha and theta activity, athletes can alleviate stress and anxiety.
- Cognitive Performance: Enhanced cognitive functions such as decision making and reaction time can result.
Technological Advancement:
- Improvements in portable EEG devices have rendered neurofeedback more available for athletes.
- Biofeedback and neurofeedback can be utilized together to offer a holistic approach to enhancing performance. For instance, an athlete may employ EMG to decrease muscle tension while concurrently using EEG to enhance brainwave patterns for concentration.
- It is vital to recognize that these methods are at their most effective when incorporated into a thorough psychological skills training regimen.
Conclusion
Biofeedback and neurofeedback serve as effective resources for athletes aiming to boost performance by refining physiological and neurological conditions. Through obtaining awareness and control over these processes, athletes can elevate their capacity to handle stress, improve concentration, and reach optimal performance. The ideas presented in the supplied texts endorse the notion that both mental and physical conditions can be developed, and that regulating these conditions is crucial for achieving athletic success.
References
- Cox, R. (2006). Sport Psychology. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Jarvis Matt (2006). Sport Psychology : A student’s Handbook. Routledge.
- Weinberg, R. S., & Gould, D. (2019). Foundations of Sport and Exercise Psychology. Human Kinetics.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 15,195 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, March 29). Biofeedback and Neurofeedback: 2 important techniques to enhance athlete’s performance. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/biofeedback-and-neurofeedback/
