Understanding Arousal & Performance
Arousal is a general physiological and psychological activation of the organism that varies on a continuum from deep sleep to intense excitement. It involves changes in physiological responses (heart rate, respiration, muscle tension) and psychological states (alertness, focus). To optimize the performance of an athlete it is necessary to maintain balance between arousal states. Extreme arousal often leads to inefficient game, hence different arousal relaxation techniques are found to be very useful for the athletes.
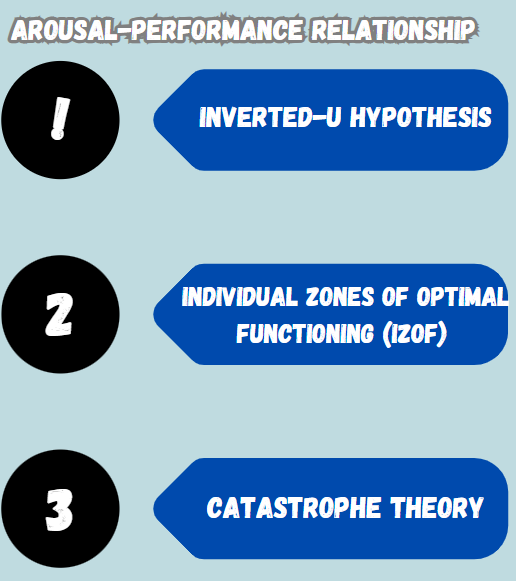
Arousal-Performance Relationship:
Inverted-U Hypothesis
- Performance often enhances as arousal rises until it reaches an ideal level.
- After this level, additional increases in arousal result in a drop in performance.
- The ideal arousal level differs based on:
- The individual: Certain athletes excel in high-pressure situations, whereas others do better with less arousal.
- The task: Tasks that involve complex or fine motor skills need lower arousal, while gross motor skill tasks might gain from increased arousal.
Individual Zones of Optimal Functioning (IZOF) – Hanin
- This theory posits that every athlete possesses a distinct spectrum of arousal levels in which they achieve peak performance.
- Instead of one specific optimal point, there exists a zone of optimal functioning.
- It emphasizes individual emotional patterns and their connection to performance.
Catastrophe Theory- Hardy
- Suggests that when cognitive anxiety (worry) is high, rises in physiological arousal may result in a sudden and significant drop in performance (a “catastrophe”).
- After the catastrophic decline happens, it becomes quite challenging to regain the same level of performance.
Relaxation Techniques
Purpose: To decrease excessive stimulation, control anxiety, and improve performance.
Deep Breathing
Mechanism: Gradual, profound breaths stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which opposes the impacts of the sympathetic nervous system (fight-or-flight response).
Technique:
- Breathe in gently and deeply through the nostrils, expanding the abdomen.
- Pause for a few moments.
- Breathe out gently through the mouth.
- Concentrate on the feeling of your breath.
- Can be utilized prior to, throughout, and following performance.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) (Jacobson)
Mechanism: Entails systematically tightening and relaxing various muscle groups to enhance awareness of muscle tension and facilitate relaxation.
Technique:
- Begin with the feet and proceed upward through the body.
- Contract each muscle group for 5-10 seconds, then let go and relax for 20-30 seconds.
- Concentrate on the contrast between tension and relaxation.
- Can be practiced in a tranquil environment.
Autogenic Training (Schultz and Luthe)
Mechanism: Utilizes self-hypnosis and verbal prompts to create sensations of warmth and weight in the limbs and body, resulting in relaxation.
Technique:
- Includes repeating statements like “My right arm is heavy” or “My forehead is cool. “
- Demands practice to achieve proficiency.
- Encourages both physiological and psychological relaxation.
Meditation and Mindfulness:
Mechanism: Entails concentrating attention on the current moment without judgment, minimizing rumination and anxiety.
Mindfulness:
- Focusing on thoughts, feelings, and sensations in a non-reactive manner.
- Enhances self-awareness and emotional management.
- Can be practiced through structured meditation or casual mindfulness activities (e. g. , mindful walking, mindful eating).
Meditation:
- Typically involves concentrating on the breath, a mantra, or a visual image.
- Seeks to calm the mind and reach a state of profound relaxation.
- Aids in reducing anxiety and enhancing focus.

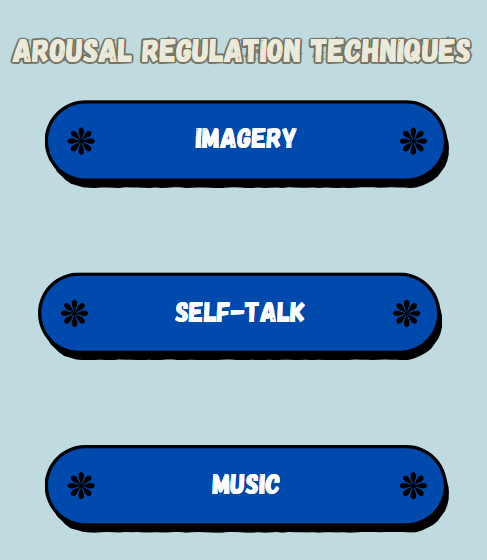
Arousal Regulation Techniques
Purpose: To raise arousal when it is insufficient, or to sustain ideal arousal levels.
Imagery
Mechanism: Generating vivid mental images of successful execution to boost motivation and arousal.
Technique:
- Envision executing the skill successfully, emphasizing the sensory experiences (sight, sound, feel).
- Can be applied to enhance confidence and mental preparedness.
Self-Talk:
Mechanism: Employing positive and encouraging self-statements to improve arousal and concentration.
Technique:
- Recognize negative self-talk and substitute it with positive affirmations (e. g. , “I can do this,” “I am strong”).
- Utilize cue words to elicit desired emotions or behaviors.
Music:
Mechanism: Listening to music can affect arousal levels, based on the tempo and genre.
Technique:
- Incorporate upbeat, lively music to elevate arousal prior to competition.
- Incorporate soothing music to diminish arousal and anxiety.
Physical Activity
Mechanism: Participating in warm-up exercises or physical activity can heighten physiological arousal.
Technique: Dynamic warm-ups, brief sprints, or other activities to elevate heart rate and alertness.
Applying Relaxation and Arousal Techniques
Individualization
The most effective techniques differ from athlete to athlete. Athletes should try out various methods to discover what is most effective for them.
Practice
Relaxation and arousal regulation techniques need regular practice to be effective. Athletes should weave these techniques into their training programs.
Pre-Performance Routines
Creating a reliable pre-performance routine can assist athletes in controlling arousal and enhancing performance. This routine may consist of a mix of relaxation and arousal regulation strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehending the connection between arousal and performance is vital for enhancing athletic performance.
- Relaxation methods can assist athletes in handling anxiety and minimizing excessive arousal.
- Arousal management strategies can aid athletes in boosting arousal when necessary and sustaining optimal levels.
- Personalization and regular practice are critical for the effective application of these techniques.
References
- Cox, R. (2006). Sport Psychology. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Jarvis Matt (2006). Sport Psychology : A student’s Handbook. Routledge.
- Weinberg, R. S., & Gould, D. (2019). Foundations of Sport and Exercise
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 15,136 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, March 28). 3 important Arousal & Relaxation Techniques to enhance performance. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/arousal-relaxation-techniques/
