Aggression in sports is a multifaceted and frequently debated subject. Although a certain degree of assertiveness and competitive spirit is crucial for achieving athletic success, the distinction between these constructive traits and intolerable aggressive conduct can be vague. This study guide investigates the essence of aggression in sports, analyzing its different manifestations, root causes, and possible repercussions, based on insights from the literature on sport psychology.
Defining Aggression in Sports
It’s crucial to distinguish aggression from related concepts like assertiveness and competitiveness.
Assertiveness: Defined by strong behavior, a determination to succeed, and a readiness to compete. Assertiveness operates within the boundaries and does not include a desire to cause harm.
Competitiveness: An aspiration to succeed and surpass rivals. Similar to assertiveness, competitiveness doesn’t inherently include aggression.
Aggression: Actions aimed at causing damage or injury to another individual (whether physical or psychological) and frequently entails anger or hostility. The critical aspect is ‘intent’.
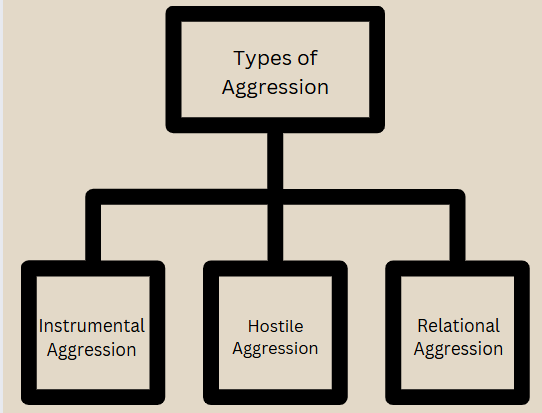
Types of Aggression in Sports
- Instrumental Aggression: Aggression employed as a method to reach a specific objective, such as winning a contest or gaining an edge. Although the action may be harmful, the main intention is not to cause pain but to attain a wanted result. For instance, a football player executing a tough tackle, even if it results in injury, to prevent a touchdown.
- Hostile Aggression: Aggression driven by anger, frustration, or a wish to cause harm. The main aim is to injure or psychologically damage the other individual. Instances include intentionally targeting an opponent’s injured area or engaging in verbal insults meant to belittle.
- Relational Aggression: Aggression focused on harming someone’s social connections or status. This can include spreading gossip, excluding someone from the group, or using social media to bully or harass. This type of aggression can be especially common in team sports.
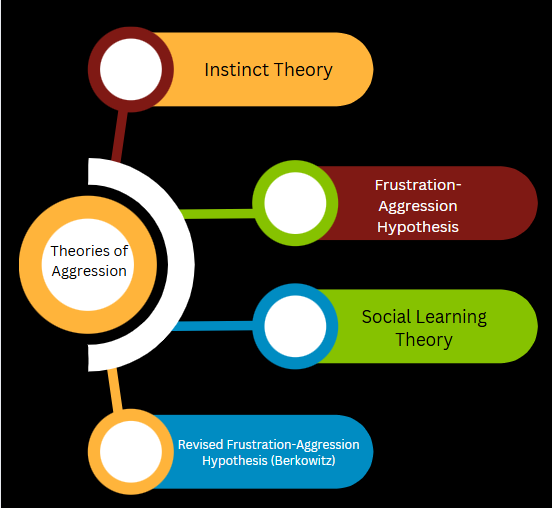
Theories of Aggression
- Instinct Theory: This theory indicates that aggression is an inherent, biological impulse. While it played a significant role in early psychology, its relevance in modern sport psychology is limited.
- Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis: This theory claims that frustration, which involves hindering goal achievement, results in aggression. Although frustration can certainly play a part in aggression, it is not the sole factor.
- Social Learning Theory: This theory highlights the significance of learning through observation and rewards. Individuals acquire aggressive behaviors by watching others, especially role models, and receiving reinforcement for aggressive actions. This theory is well-supported in elucidating aggression in sports, as athletes may adopt aggressive strategies from coaches, teammates, or even media representations of sports.
- Revised Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis (Berkowitz): This theory posits that frustration results in aggression only when specific cues are present, such as the existence of a weapon or a perceived provocation. This underscores the significance of contextual factors in inciting aggressive behavior.
Factors Influencing Aggression in Sports
- Situational Factors: The environment of the game, including the score, the significance of the match, the presence of competitors, and the officiating, can all impact aggression.
- Personal Factors: Variations in individual personality traits, such as trait aggression, competitiveness, and emotional management, can influence the probability of aggressive conduct.
- Social Factors: Team norms and values, the impact of coaches and peers, and societal expectations related to masculinity and athletics can all contribute.
- Media Influence: Exposure to aggressive or violent content in the media, encompassing sports broadcasts, can aid in the learning and normalization of aggressive behavior.

Consequences of Aggression in Sports
Aggression in sports can have numerous negative consequences:
- Injuries: Hostile behavior can result in physical harm for both the perpetrator and the target.
- Penalties and Suspensions: Hostile actions may lead to penalties, fines, and suspensions, affecting team performance and individual careers.
- Reputational Damage: Athletes and teams recognized for hostile behavior may experience reputational harm, influencing sponsorships and public perception.
- Legal Issues: In some situations, serious acts of hostility can result in legal charges and criminal prosecution.
- Psychological Impact: Hostility can bring about negative psychological consequences for both the perpetrator (e. g. , guilt, shame) and the target (e. g. , fear, anxiety).
Managing Aggression in Sports
Several strategies can be employed to manage and reduce aggression in sports:
- Education and Awareness: Informing athletes, coaches, and parents about the characteristics of aggression, its impacts, and ways to handle it.
- Rule Enforcement: Regularly and impartially applying rules to discourage aggressive conduct.
- Developing Emotional Regulation Skills: Instructing athletes in methods for coping with anger, frustration, and other feelings that may lead to aggression.
- Promoting Positive Role Models: Showcasing athletes and coaches who exemplify sportsmanship and moral conduct.
- Creating a Positive Team Climate: Cultivating a team environment that prioritizes respect, collaboration, and fairness.
- Stress Management Techniques: Teaching athletes methods for handling stress and pressure, which can occasionally incite aggression.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Assisting athletes in altering negative thoughts and perceptions that may lead to aggression.
Conclusion
Aggression in sports is a complex challenge with various causes and effects. While a degree of assertiveness and competitiveness is crucial for success in athletics, aggressive actions meant to inflict harm are inappropriate in sports. By grasping the different types of aggression, the elements that lead to it, and suitable management tactics, coaches, athletes, and other parties can collaborate to establish a safer and more encouraging sports atmosphere. The emphasis should be on encouraging ethical conduct, enhancing emotional regulation abilities, and cultivating a culture that prioritizes respect and fair competition.
Read : Prevention and Reduction of Aggression
References:
- Cox, R. (2006). Sport Psychology. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Jarvis Matt (2006). Sport Psychology : A student’s Handbook. Routledge.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 16,508 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, March 27). Aggression in Sports: 4 important theories of aggression. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/aggression-in-sports/
