Introduction
Neurolinguistic Programming (NLP) is a psychological approach that explores the connection between neurological processes, language, and behavioral patterns learned through experience. It is based on the premise that people can improve their communication skills, personal development, and even therapeutic interventions by understanding and modifying their thought patterns and behaviors. NLP has been widely used in various fields, including therapy, business, education, and self-improvement.
Read More- Chomsky’s Lingusitic Theory
History of Neurolinguistic Programming
NLP was developed in the 1970s by Richard Bandler, a computer science student, and John Grinder, a linguistics professor, at the University of California, Santa Cruz. They were influenced by the works of famous therapists such as Fritz Perls (Gestalt therapy), Virginia Satir (family therapy), and Milton Erickson (hypnotherapy).

Grinder and Bandler
Bandler and Grinder aimed to identify the patterns and strategies used by these successful therapists and translate them into models that others could learn and apply. Their first book, The Structure of Magic (1975), laid the foundation of NLP by demonstrating how language and behavior influence human experiences.
Over the years, NLP evolved into a set of techniques and models that claim to improve communication, change limiting beliefs, and enhance personal and professional growth. However, despite its popularity, NLP has also faced significant criticism regarding its scientific validity and empirical support.

Neurolinguistic Programming
Principles of Neurolinguistic Programming
NLP operates on several core principles that guide its methodology-
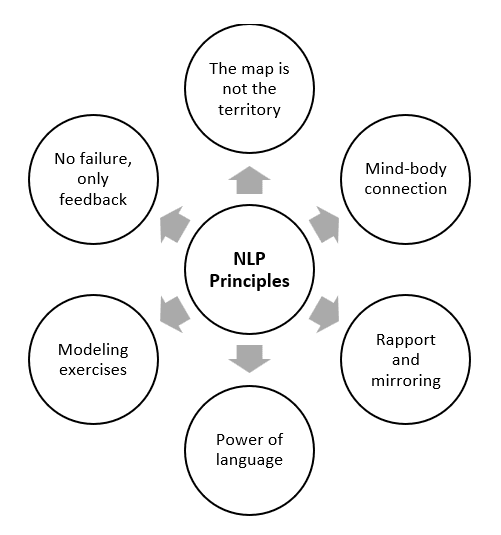
NLP Principles
- The Map is Not the Territory- This concept, derived from Alfred Korzybski’s General Semantics, suggests that individuals perceive reality through their subjective experiences, or “maps.” Since no two individuals share the exact same perceptions, NLP aims to help people modify their mental maps to achieve better outcomes.
- The Mind-Body Connection- NLP asserts that thoughts, emotions, and physical states are interconnected. By changing one’s thoughts or physiology, individuals can influence their emotions and behavior.
- Rapport and Mirroring- Effective communication is based on building rapport. NLP practitioners use techniques like mirroring (subtly imitating body language, tone, and speech patterns) to establish trust and connection.
- The Power of Language- Language shapes thoughts and behaviors. NLP emphasizes the use of precise language patterns to reframe limiting beliefs and encourage positive change.
- Modeling Excellence- One of the fundamental tenets of NLP is that success can be replicated by studying and modeling the behaviors, beliefs, and strategies of successful individuals.
- There is No Failure, Only Feedback- NLP promotes the idea that setbacks should be seen as learning opportunities rather than failures. By analyzing feedback, individuals can adapt and improve their strategies.
NLP Techniques and Methods
NLP encompasses a variety of techniques designed to facilitate personal transformation. Some of the most common techniques include-
- Anchoring- Anchoring involves associating a physical stimulus (e.g., touching a specific part of the body) with a desired emotional state. By repeatedly triggering the anchor, individuals can recall positive emotions on demand.
- Reframing- Reframing is a technique that helps individuals change their perspective on a situation. For example, a person experiencing anxiety about public speaking might reframe their nervousness as excitement, which can lead to a more confident presentation.
- Swish Pattern- The Swish Pattern is used to replace undesirable habits or thought patterns with more empowering alternatives. This technique involves visualizing a negative behavior being replaced by a positive one in a rapid and automatic manner.
- Meta Model- The Meta Model is a linguistic tool that helps uncover deep-seated beliefs and assumptions by questioning vague or limiting language. It aims to bring clarity and expand perspectives.
- Milton Model- Named after Milton Erickson, this technique employs vague and metaphorical language to encourage subconscious change, often used in hypnosis and therapy.
- Visualization and Mental Rehearsal- NLP practitioners encourage individuals to visualize successful outcomes in vivid detail, reinforcing positive expectations and behaviors.

Mental Rehersal and Skill Acquisition
Applications of Neurolinguistic Programming
Some applications of neurolinguistic programming include-
- Therapy and Counseling- NLP is used in psychotherapy to help individuals overcome phobias, trauma, anxiety, and depression. By changing the way individuals process their experiences, NLP techniques can promote emotional healing.
- Business and Leadership- Many professionals use NLP for improved communication, negotiation, and leadership skills. Salespeople, for instance, use NLP to build rapport with clients and influence decision-making.
- Education and Learning- Teachers and educators incorporate NLP techniques to enhance learning experiences. Strategies like visualization and anchoring help students retain information more effectively.
- Personal Development and Coaching- Life coaches and motivational speakers frequently use NLP to empower individuals to achieve personal and professional goals. Techniques such as goal-setting, modeling, and state management help clients enhance their performance.
- Health and Well-being- NLP has been applied in areas such as pain management, weight loss, and stress reduction. By reframing beliefs about health and using visualization techniques, individuals can develop healthier habits.
Criticism
Despite its widespread popularity, NLP has been criticized for its lack of scientific validation. Several key criticisms include-
- Lack of Empirical Evidence- Many scientific studies have found limited or no evidence to support NLP’s effectiveness. A systematic review by Witkowski (2010) concluded that NLP lacks credible scientific backing.
- Pseudoscientific Claims- NLP’s claims, such as the ability to cure phobias instantly or detect lies through eye movements, have been debunked by researchers (Heap, 2008).
- Inconsistent Methodology- NLP lacks a standardized methodology, leading to variations in training and practice. This inconsistency makes it difficult to measure its true effectiveness.
- Commercialization and Exaggeration- NLP is often marketed as a quick-fix solution, leading to exaggerated claims that diminish its credibility. Many training programs are profit-driven, prioritizing business over scientific rigor.
Conclusion
Neurolinguistic Programming remains a popular yet polarizing field. While its techniques have been widely adopted in personal development, therapy, and business, its scientific credibility is frequently questioned. Understanding both its strengths and limitations is crucial for anyone looking to explore NLP.
For those interested in NLP, it is recommended to approach it with a critical mindset, seeking evidence-based applications while being cautious of exaggerated claims. Whether as a tool for self-improvement or a subject of academic debate, NLP continues to provoke interest and discussion in the fields of psychology and human behavior.
References
Bandler, R., & Grinder, J. (1975). The Structure of Magic: A Book About Language and Therapy. Science and Behavior Books.
Heap, M. (2008). The validity of some early claims of neuro-linguistic programming. Skeptical Intelligencer, 11, 12-14.
Witkowski, T. (2010). Thirty-five years of research on NLP: Time for a change. Polish Psychological Bulletin, 41(2), 58-66.
Korzybski, A. (1933). Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics. Institute of General Semantics.
Dr. Balaji Niwlikar. (2025, February 10). What is Neurolinguistic Programming and Its 5 Important Applications. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/neurolinguistic-programming/
