“Coping” is defined as the cognitive, behavioral, and emotional efforts taken in response to demands perceived by him as taxing or exceeding his resources.
Types of Coping Methods
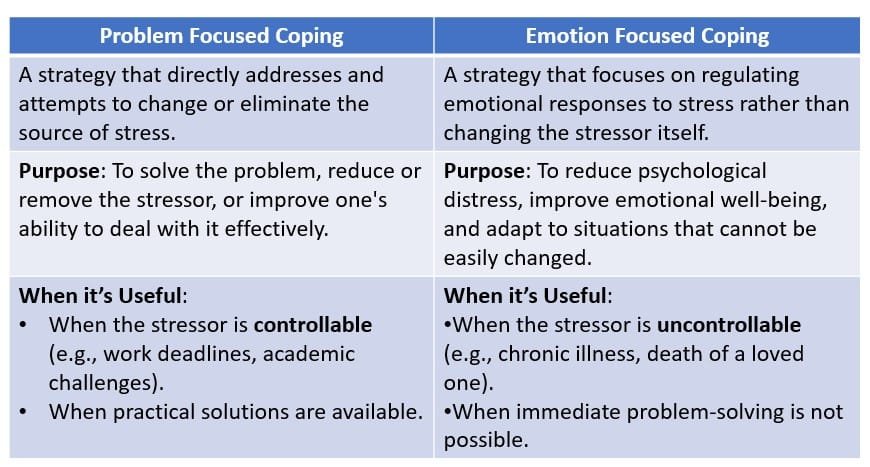
- Problem-Focused Coping : Directly addressed to deal with the stressor at issue.
- Involves identifying the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating the pros and cons of each, and then putting the chosen one into operation.
- Most effective if the stressor is within one’s control.
For example-
- Planning a study schedule for exam stress.
- A direct negotiation with a colleague to resolve the conflict.
- Seeking information or counsel about aspects of one’s life that cause stress.
- Time Management
2. Emotion-Focused Coping: Emotion-focuses the stress distress expressed.
- Regulation of emotions such as anxiety, anger, or sadness.
- More effective when the stressor is uncontrollable.
For examples:
- Relaxation techniques (deep breathing, meditation).
- Seeking social support from family or friends.
- Using cognitive reappraisal (reframing negative thoughts).
- Distraction (watching a movie, listening to music).
- Physical exercise.
3. Cognitive-Behavioral Coping: A mental approach aimed at modifying the person’s view regarding the stressful situation in question.
- Challenging one’s own irrational or negative thoughts and assuming a perspective more positive or rational in nature.
For examples:
- Cognitive restructuring (identifying and changing maladaptive thought patters).
- Finding humour in a situation.
- Finding something positive in a stressful experience.
Additional Coping Strategies and Considerations:
- Social Support:
Social support is one of the greatest coping mechanisms. Humans are primarily social beings, and the support network plays an extremely important role in buffering stress-induced negative impacts.
There are different kinds of social support:
- Emotional support: Empathy, care, and concern.
- Tangible support: Practical help, such as lending money or assistance with tasks.
- Informational support: Advice or guidance.
- Individuals with strong support in place and those who can call on help with their problems generally suffer less stress and enjoy better health and health practices.
- Relaxation Techniques:
Techniques are very effective stress-reducing mechanisms. The great relaxation techniques activate the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a state of calm and relaxation.
- Meditation: Concentration on a single point of reference, such as breath or a word that quiets the mind.
- Yoga: A blending of postures, breathing exercises, and meditation aimed at enhancing the health of both body and mind.
- Deep breathing: Slow, deep breaths can reduce physiological arousal.
- It emphasizes that when these techniques are done regularly, the stress levels, anxiety, and general health would improve.
- Workout (Exercise):
- This is for sure a main area of personal training for stress management.
- Exercise releases into the bloodstream the endorphins, which signify to the body that it is in a good mood. It grounds focus on something outside a stressful situation while also providing better conditions for health.
- All kinds of movement are commonly presented as useful tools for stress and enhancement of the overall well-being of an organism.
- Time Management:
Properly managing time can act along different premises whereby it becomes an effective tool in minimizing stress mainly on a student-hosted basis. Effective time management involves:
- Setting priorities.
- Breaking down large tasks into smaller ones able to be done separately.
- Avoiding procrastination.
- Using organizational tools.
- Better time management reduces the sense of being overwhelmed and the feeling of control, which consequently reduces stress levels.
- Avoidance Coping:
- As a strategy for mainly coping with stress via reductive means.
- In avoiding coping, a person such as the pregnant woman may attempt to escape the stressors or blindly ignore them. It may prove to be of some comfort in the short run, but in the long haul, it becomes detrimental.
- That avoidance coping does not motivate one to solve or deal with the real problems that create stress and can even increase anxiety or further psychological problems.
- Defense Mechanisms:
- The concept of defense mechanisms, which are unconscious psychological processes used to protect oneself from anxiety.
- They explain that defense mechanisms can be adaptive in certain situations, but overreliance on them can be problematic.
- Examples of defense mechanisms discussed in their text include:
- Repression: Unconsciously blocking distressing thoughts or memories.
- Denial: Refusing to acknowledge reality.
- Projection: Attributing one’s own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to others.
- Mindfulness:
- Mindfulness as a valuable technique for stress reduction and emotional regulation.
- Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment.
- Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and mindful breathing, can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings, allowing them to respond to stress in a more adaptive way.
- Resilience:
- Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity.
- They highlight the importance of resilience in coping with stress and overcoming challenges.
- Factors that contribute to resilience include:
- Positive self-esteem.
- Optimism.
- Social support.
- Effective coping skills.
Stress relief
Factors Influencing Coping Effectiveness:
- Controllability of the stressor: Problem-focused coping is more effective for controllable stressors, while emotion-focused coping is better for uncontrollable stressors.
- Individual differences: Personality, coping style, and available resources can influence coping effectiveness.
- Cultural factors: Cultural norms and values can influence the types of coping strategies people use.
Therefore, these are coping strategies used for stress management.
References:
- Ciccarelli, S, & White, J, N. (2017). Psychology. Global Edition, Pearson: libgen.lc
- Egyankosh : Stress and its management
Dr. Balaji Niwlikar. (2025, February 4). 3 Key Coping Strategies for Stress. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/3-key-coping-strategies-for-stress/
