Introduction
Trauma is a deeply distressing experience that significantly impacts an individual’s emotional, psychological, and physical well-being. It can result from a single overwhelming event or prolonged exposure to adverse circumstances. Trauma-related disorders, such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), Acute Stress Disorder (ASD), and Complex PTSD, can have profound and long-lasting effects on individuals.
Trauma management involves trauma, helping individuals process their experiences, regulate emotions, and develop coping mechanisms to facilitate healing.
Definition of Trauma
Trauma is defined as an emotional response to a distressing event that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. According to the American Psychological Association (APA, 2020), trauma can manifest immediately or over time, influencing a person’s mental health, behavior, and social interactions.
Read More- PTSD
Types of Trauma
Trauma can be classified into three main categories:
- Acute Trauma: This results from a single distressing event, such as a car accident, a natural disaster, or a violent assault.
- Chronic Trauma: Occurs when a person is exposed to ongoing distress over a prolonged period, such as domestic violence, repeated abuse, or long-term illness.
- Complex Trauma: A combination of multiple traumatic experiences, particularly interpersonal in nature, such as childhood abuse, human trafficking, or prolonged neglect.
Common Causes of Trauma
Trauma can arise from various circumstances, including but not limited to:
- Physical, emotional, or sexual abuse
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, hurricanes)
- War, combat exposure, or terrorism
- Serious accidents (car crashes, workplace injuries)
- Life-threatening illnesses or medical procedures
- Loss of a loved one
- Witnessing violence or death
- Neglect or abandonment
The Psychological Impact of Trauma
Trauma affects key areas of the brain, including the amygdala (responsible for emotional regulation), the prefrontal cortex (associated with decision-making), and the hippocampus (involved in memory processing). This disruption can lead to:
- Emotional instability (fear, anxiety, sadness, anger)
- Hypervigilance and exaggerated startle responses
- Dissociation or emotional numbness
- Difficulty concentrating and sleeping
- Self-destructive behaviors (substance abuse, self-harm)
Trauma-Related Disorders
Trauma can lead to various mental health conditions. The most common trauma-related disorders include-
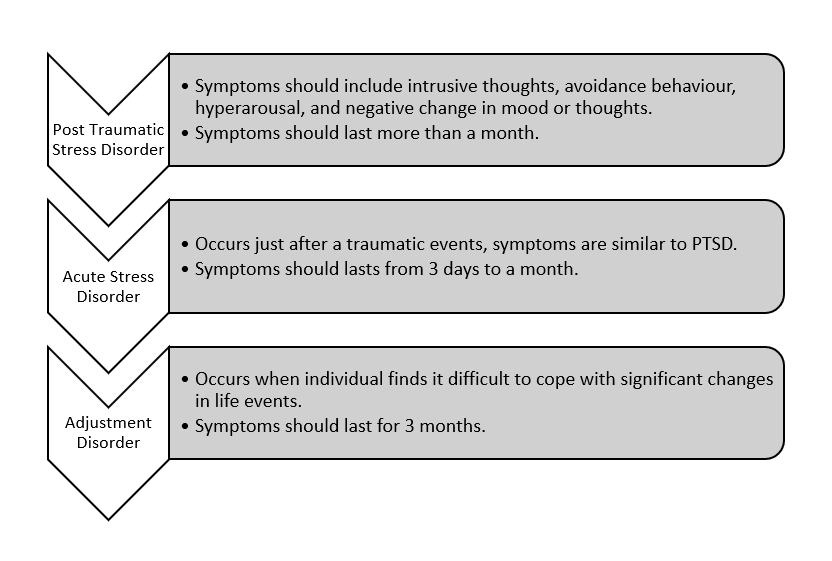
Trauma Related Disorders
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)- PTSD is one of the most severe consequences of trauma. It is characterized by-
- Intrusive Symptoms- Flashbacks, nightmares, and distressing memories.
- Avoidance Behaviors- Avoiding reminders of the trauma.
- Negative Changes in Cognition and Mood- Feelings of guilt, blame, or detachment.
- Hyperarousal- Insomnia, irritability, or heightened startle response.
The DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association, 2013) states that PTSD is diagnosed when these symptoms persist for more than a month and significantly impair daily functioning.
2. Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)- ASD occurs immediately after a traumatic event and shares symptoms with PTSD. However, ASD symptoms last between 3 days to 1 month. Early intervention can prevent ASD from developing into PTSD.
3. Adjustment Disorders- Adjustment disorders occur when individuals struggle to cope with significant life changes (e.g., divorce, job loss). Symptoms include emotional distress, anxiety, and social withdrawal.
4. Complex PTSD- Complex PTSD arises from prolonged, repeated trauma, such as childhood abuse. It includes PTSD symptoms along with-
- Emotional dysregulation
- Deep-seated feelings of guilt and shame
- Difficulty forming healthy relationships
- Dissociation and identity disturbances
Read More- Counselling for Individuals With HIV/AIDS
Counselling Techniques for Trauma Management
Counselling is a crucial component of trauma recovery. Below are evidence-based counselling techniques for trauma management-
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a structured psychotherapy approach that helps individuals identify and modify unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. It is particularly effective for trauma-related disorders.
Core Components of CBT for Trauma-
- Cognitive Restructuring- Identifying and challenging negative thoughts related to the trauma.
- Exposure Therapy- Gradual exposure to trauma-related memories and situations to reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Behavioral Activation- Encouraging engagement in positive activities to improve mood and functioning.
Studies by Foa et al. (2008) demonstrate that CBT significantly reduces PTSD symptoms by addressing cognitive distortions and avoidance patterns.
2. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR, developed by Francine Shapiro, is a trauma-focused therapy that helps individuals process distressing memories through guided eye movements.
How EMDR Works-
- The client recalls traumatic memories while engaging in bilateral stimulation (e.g., guided eye movements).
- This process reduces the emotional intensity of traumatic memories.
- The individual reprocesses the memory, integrating more adaptive beliefs.
EMDR is supported by extensive research, including studies by Shapiro (2001), confirming its effectiveness in reducing PTSD symptoms.
3. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT)
TF-CBT is a specialized approach for children and adolescents who have experienced trauma. It integrates-
- Psychoeducation about trauma and stress
- Relaxation and emotion regulation techniques
- Gradual exposure to trauma-related memories
TF-CBT has been highly effective in reducing PTSD symptoms in children (Cohen et al., 2006).
4. Stress Inoculation Training (SIT)
SIT, developed by Meichenbaum (1996), is a cognitive-behavioral therapy designed to prepare individuals for future stressors.
Three Phases of SIT-
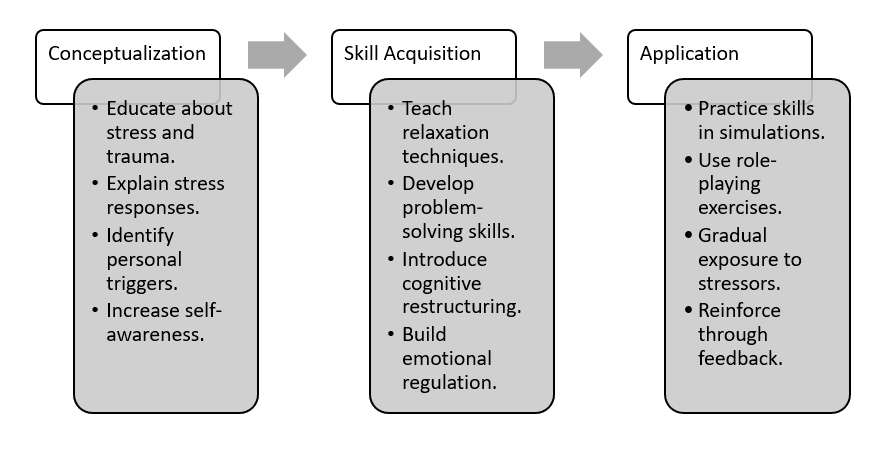
Stress Inoculation Technique
- Conceptualization Phase- Educating clients about stress responses.
- Skill Acquisition Phase- Teaching relaxation, problem-solving, and cognitive restructuring.
- Application Phase- Practicing coping skills in simulated stressful situations.
SIT has been shown to enhance resilience and prevent PTSD.
5. Supportive Psychotherapy
Supportive therapy provides emotional and social support in a warm, non-judgmental environment. Techniques include-
- Active listening and validation
- Encouraging emotional expression
- Strengthening social connections
Supportive therapy is beneficial for individuals who are not ready for structured trauma therapies.
6. Narrative Therapy

Narrative Therapy (Life Shift Therapy)
Narrative therapy helps individuals reconstruct their trauma story in a way that fosters empowerment. By externalizing their trauma, they can regain a sense of control over their lives.
7. Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation methods help regulate physiological responses to trauma. These can include-
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)- PMR, developed by Jacobson (1938), involves tensing and relaxing muscle groups, reducing tension and anxiety.
- Breathing Exercises- Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing hyperarousal.
- Yoga and Meditation- Yoga practices, such as pranayama and guided meditation, improve emotional regulation and mindfulness.
Holistic Approaches to Trauma Recovery
Trauma recovery extends beyond symptom management. Holistic approaches include:
- Mindfulness and Self-Awareness- Encouraging introspection and acceptance.
- Gratitude and Positive Affirmations- Shifting focus from trauma to strengths.
- Social Support- Encouraging connections with family, friends, and support groups.
Conclusion
Trauma and its related disorders significantly impact an individual’s well-being. However, with appropriate counselling interventions, individuals can process their trauma, develop resilience, and rebuild their lives. Evidence-based therapies such as CBT, EMDR, SIT, and relaxation techniques provide effective ways to manage trauma symptoms. By integrating psychotherapy with holistic healing practices, trauma counselling empowers individuals to recover and regain control over their lives.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.).
Cohen, J. A., Mannarino, A. P., & Deblinger, E. (2006). Treating Trauma and Traumatic Grief in Children and Adolescents.
Foa, E. B., et al. (2008). Effective Treatments for PTSD.
Jacobson, E. (1938). Progressive Relaxation.
Meichenbaum, D. (1996). Stress Inoculation Training.
Shapiro, F. (2001). Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 13,984 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, January 12). 6 Counselling Techniques for Trauma Management. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/trauma-management/
